怎样创建网站赚钱网站做直播需要资质吗
一、前言
大家好,勇哥又来分享AI模型了,前几天讯飞发布的星火大模型2.0迅速的进入了我们圈子里,为了有更多更好的模型分享给大家,分享星火大模型2.0是必须做的,我做一个传递着,希望大家也星火相传啊。
我是用了几天了,所以我总结了一些科大讯飞的人工智能大模型星火大模型2.0的主要优势:
1. 多项技术专利获得:科大讯飞已经数次稳居AI专利申请第一名,对于技术的持续研发和产出让星火大模型的持续演化拥有了较为有力的支撑。
2. 前沿技术积累:科大讯飞在中文预训练模型方向已深耕多年,星火大模型2.0作为讯飞首个千亿级深度知识增强大模型,能够支持多语言接入、多任务融合和多模态整合,并持续引入业界前沿技术,持续探索和开拓AI前沿技术。
3. 强大的知识增强能力:科大讯飞的人工智能大模型基于通用型的深度学习模型,结合了知识增强、多任务训练和跨模态融合等技术,能够更好地理解和处理自然语言,包括语音识别、文本生成、图像识别等任务。
4. 丰富的应用场景:科大讯飞的人工智能大模型已经在多个领域得到了应用,如智能语音、智能客服、智能教育、智能医疗等,并已经在工业、农业、能源、环保等传统行业得到了应用。
以上4点是我总结的,当然,科技在发展,人类在进步,星火大模型还会有3.0/4.0……很多的版本,期待他会给我们带来更多的惊喜。
二、权威数据测评结果
以下信息来自【经济参考报】,具体是来自于2023年的8月《人工智能大模型体验报告2.0》,可去校验一番,数据是准确的,我没有任何改动。
原文链接:https://xhpfmapi.xinhuaxmt.com/vh512/share/11634934?channel=weixin
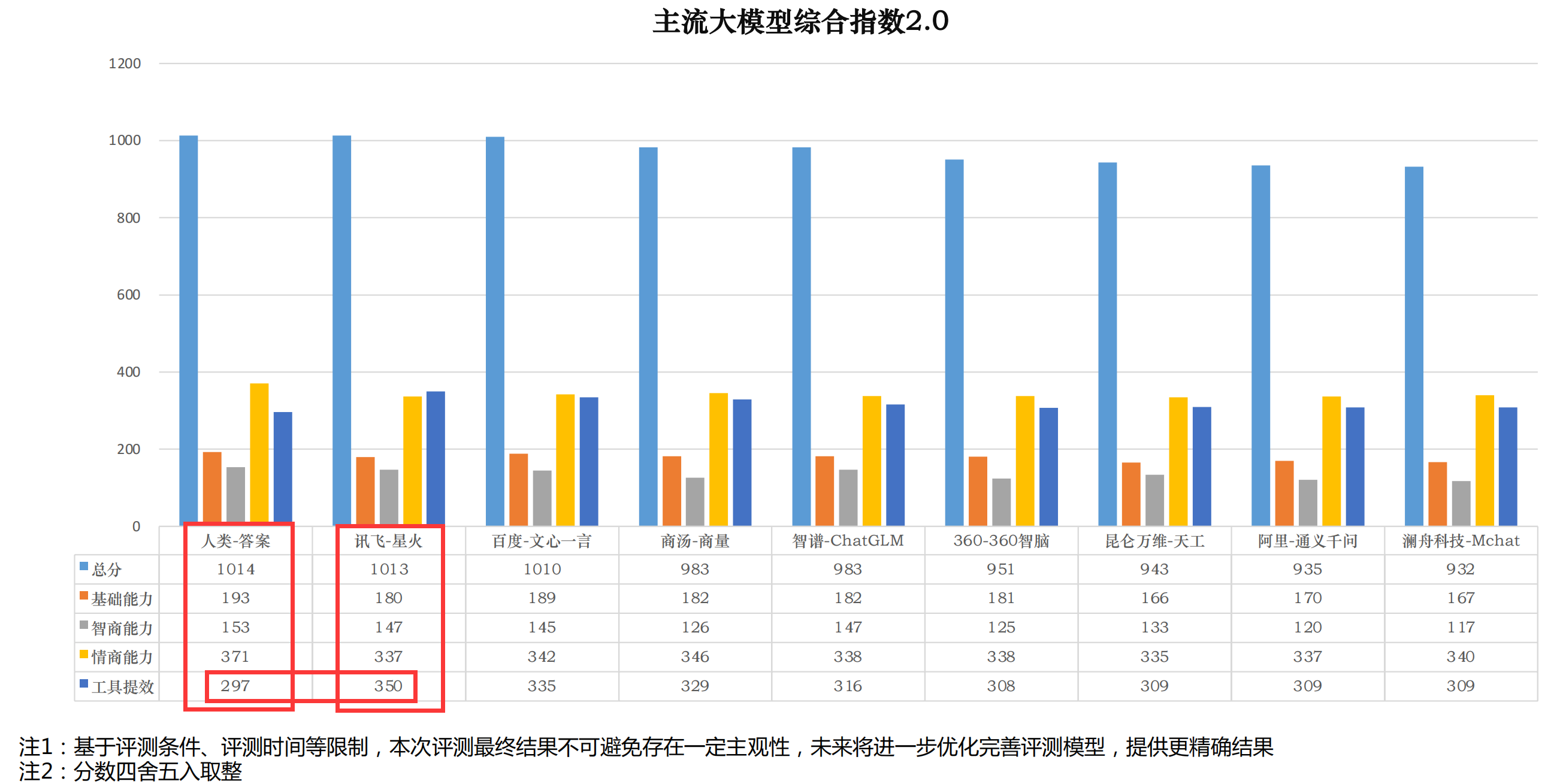
可以在上图看到讯飞星火仅仅比人类的答案少一分,【工具提效】能力碾压全场,super VIP必须稳拿。
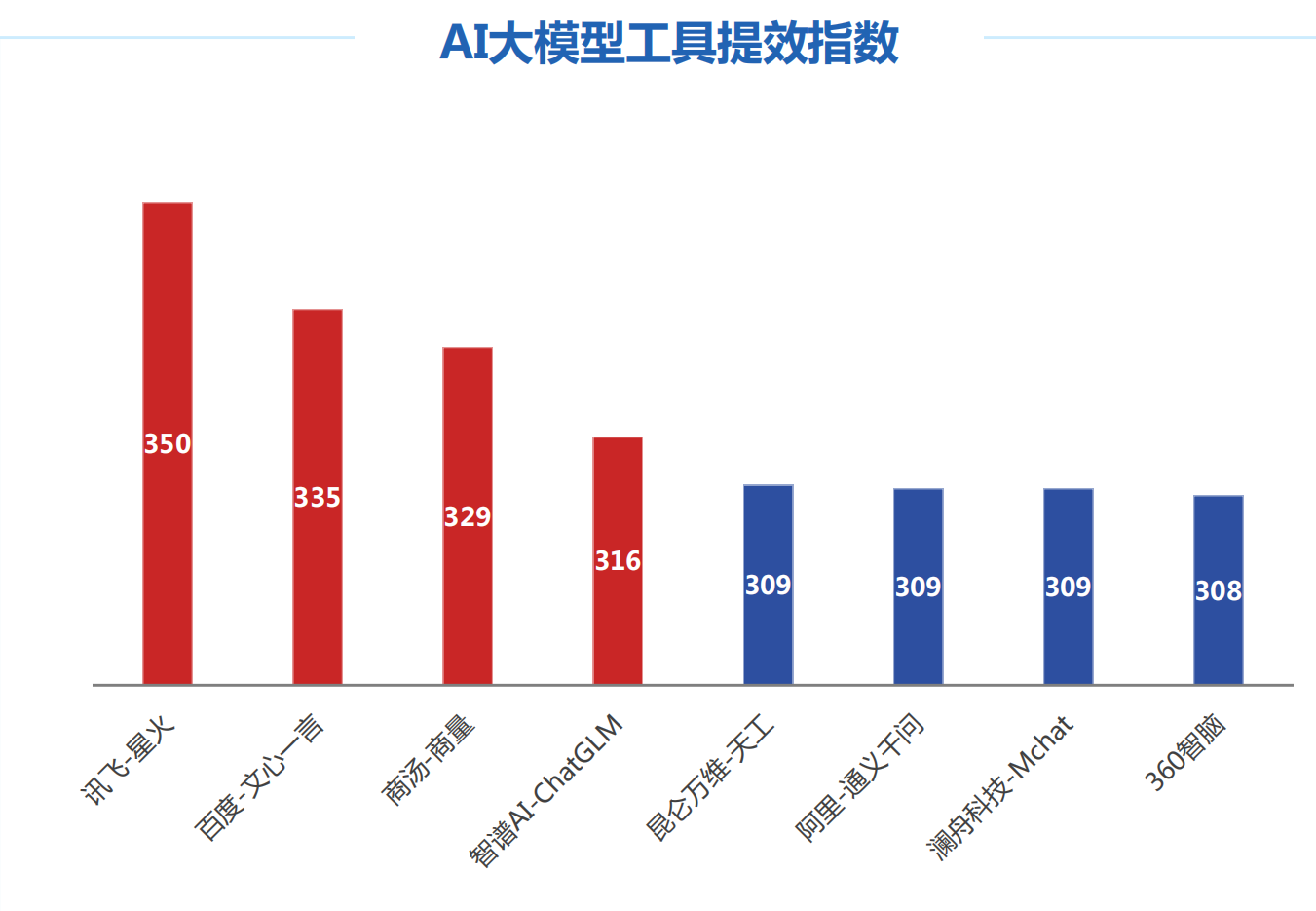
2.1 工具提效指标描述
大模型的工作提效考察通常包括两个方面:工具和创新。
工具提效是指大模型是否能够提供有效的工具来提高工作效率。这些工具可以
包括代码自动生成、数据自动分析和可视化工具、自然语言处理、文件整理、
关键内容总结整合和机器翻译工具等。具备这些工具的大模型可以帮助人们更 快地完成工作任务,提高工作效率,也是大模型最先落地的方向之一。
生成创新方面是指大模型是否能够提供新的思路和方法,推动工作方式的改进 和升级。这些创新可以包括新的业务流程、选题的创新、内容的创新等。AIGC
能力能够帮助人们打破传统的工作方式,推动工作效率提升。
权重占比:工具提效(50%)、生成创新(50%)
三、多模态功能
单独的解释【多模态功能】
多模态能力是指处理和理解多源模态信息的能力,包括文本、图像、视频、音频等不同类型的数据。多模态机器学习旨在通过机器学习的方法实现处理和理解多源模态信息的能力。目前比较热门的研究方向是图像、视频、音频、语义之间的多模态学习。
【讯飞星火认知大模型】具有7大核心能力,即文本生成、语言理解、知识问答、逻辑推理、数学能力、代码能力、多模态能力。这也是一会我们需要测试的功能。
它拥有跨领域的知识和语言理解能力,能够基于自然对话方式 理解与执行任务。从海量数据和大规模知识中持续进化,实现从提出、规划到解决问题的全流程闭环。
四、火星大模型2.0测试
火星大模型2.0的优势以及排名我都已经给大家说明了,那么接下来我们来具体测试啊。
测试步骤
官网地址:注册后点击到【进入体验】即可。

我们可以看到有星火助手,这个地方可以有很多的提示内容帮我们快速定位我们要解决的问题。
4.1 数学能力
数学可以说是我们理科和工科一切的起始点,所以我们先来测试这个。

测试内容:【出一道微积分的倒数题目,难度中等,并给出解题完整步骤。】

我们可以看到整个题目的解法步骤,给的很清晰。计算【π】的方法给的也不错。

4.2 七夕测试
测试的语句相对难度较大,我加了很多修饰词。
【今年七夕最好的礼物是什么,对方女性,25岁,温柔姌嫋,娉婷独立的样子,职场女性。】

这个难度比较大,没有给出唯一的答案,给了10条帮助选择,起始,这些和我们人自己答的也都差不多,还不错,这个瑜伽课程是想不到了。
4.3 图片生成
测试文字【帮我绘制一张真人照片,有飞雪,有戴露趾手套的女孩子,浅黄色短发,双眼有神,黑瞳,樱桃口,精致一些,高清的图片,粉色有帽子的毛衣,向手中哈气,抬头35度角的侧颜照。】,我们依次对照一下。
1、真人(符合)
2、飞雪(符合)
3、有戴露趾手套的女孩子(70%)
4、浅黄色头发(符合)
5、双眼有神,黑瞳,樱桃口(符合)
6、粉色有帽子的毛衣(符合)
7、向手中哈气(不符合)
8、抬头35度角侧颜照(80%)

整体对比下来还是非常不错的呢。我们也可以多生成几次,按钮我在途中框选了,找个合适的留图即可。
4.4 语音生成
可以直接生成语音,这个比其它平台的好太多,我就不说跟谁对比了,咱们试用一下就清楚了。

来个难为它的测试内容【生成一段女生夹子音的给175岁爷爷拜寿语音。】

可以自己去听听啊,挺好玩的呢。
4.5 视频生成
测试文本【生成一段15秒的慢三舞蹈视频。】

点开视频效果如下:

讲解了慢三舞蹈,AI讲解员也是非常哇塞的哦。
4.6 PPT生成
我们在进入的时候可以【选择插件】,我这里用生成PPT测试一下。
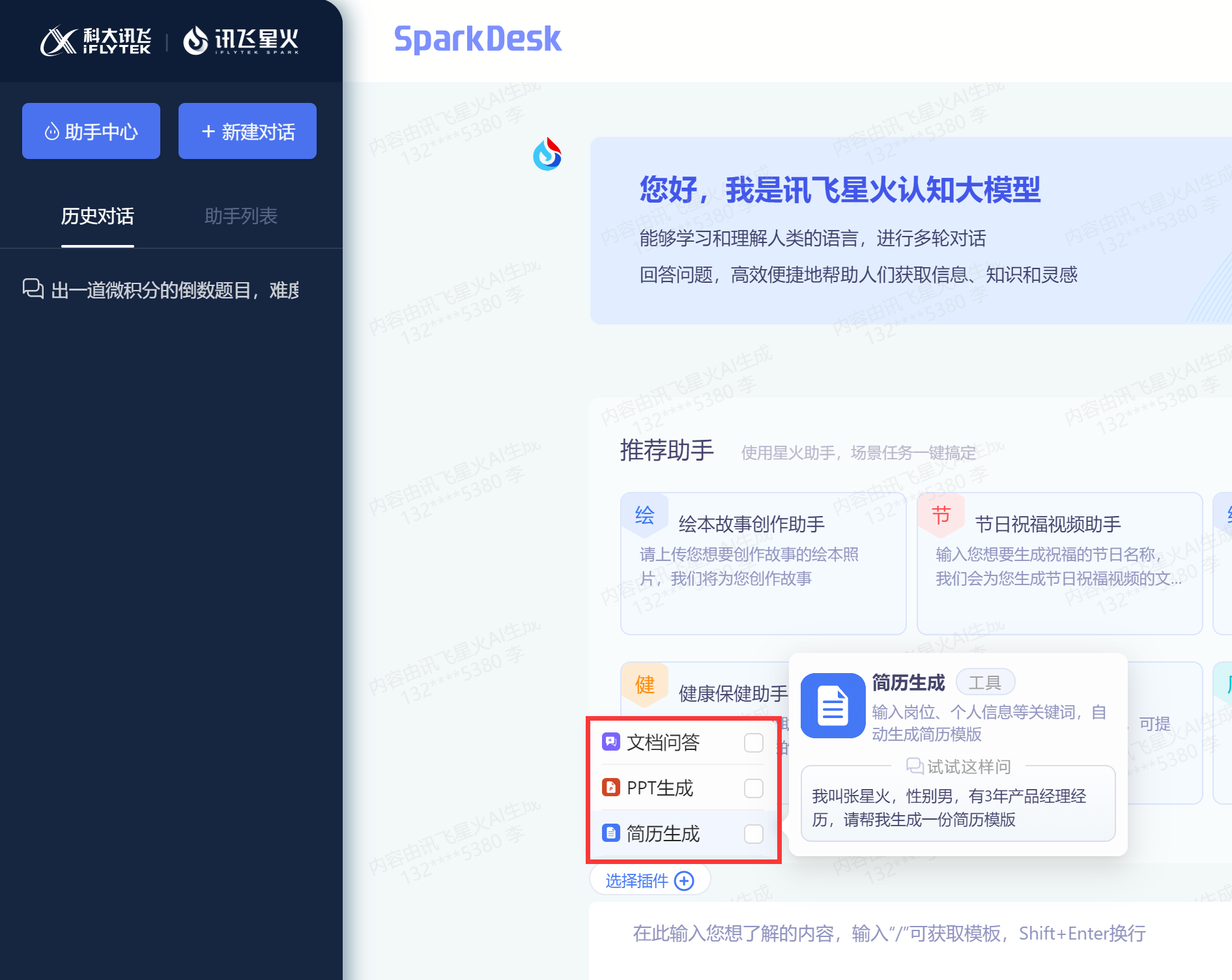
测试文本【生成一份Linux基础的文件操作PPT,页数在15页以内。】

下载看效果:

生成效果还是非常不错的呢,整个内容算是很完整的。
4.7 代码生成
为了测试难度大一些,我选择测试汇编语言。
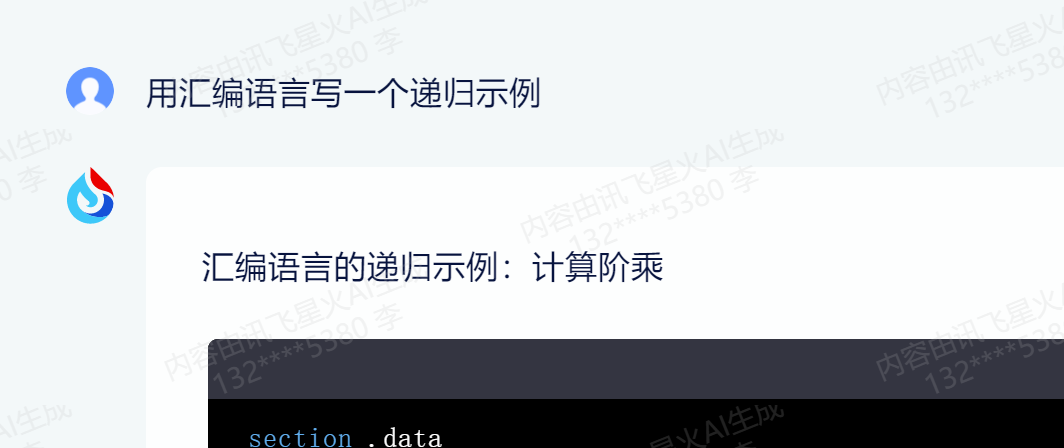
生成的代码,就算不会汇编语言,但是起码知道【;】是汇编的注释,所以下面的代码没问题,肯定是汇编的。
Bash
section .dataresult db 1section .textglobal _start_start:; 调用递归函数mov eax, 5call factorial; 退出程序mov eax, 1xor ebx, ebxint 0x80; 递归函数
factorial:cmp eax, 1jle end_recursiondec eaxpush eaxcall factorialpop eaxadd esp, 4imul dword [result], eax
end_recursion:ret
4.8 小说助手
小说助手的类型还是比较多的呢。
现在我们看小说,很多的时候看的都是爽文,也就是自己最喜欢的类型文章,所以生成的时候就可以根据自己当时的想法来生成,我们来试试。
测试内容:【生成一本关于穿越成水浒传中武松的以单挑方腊全身而退的小说。】
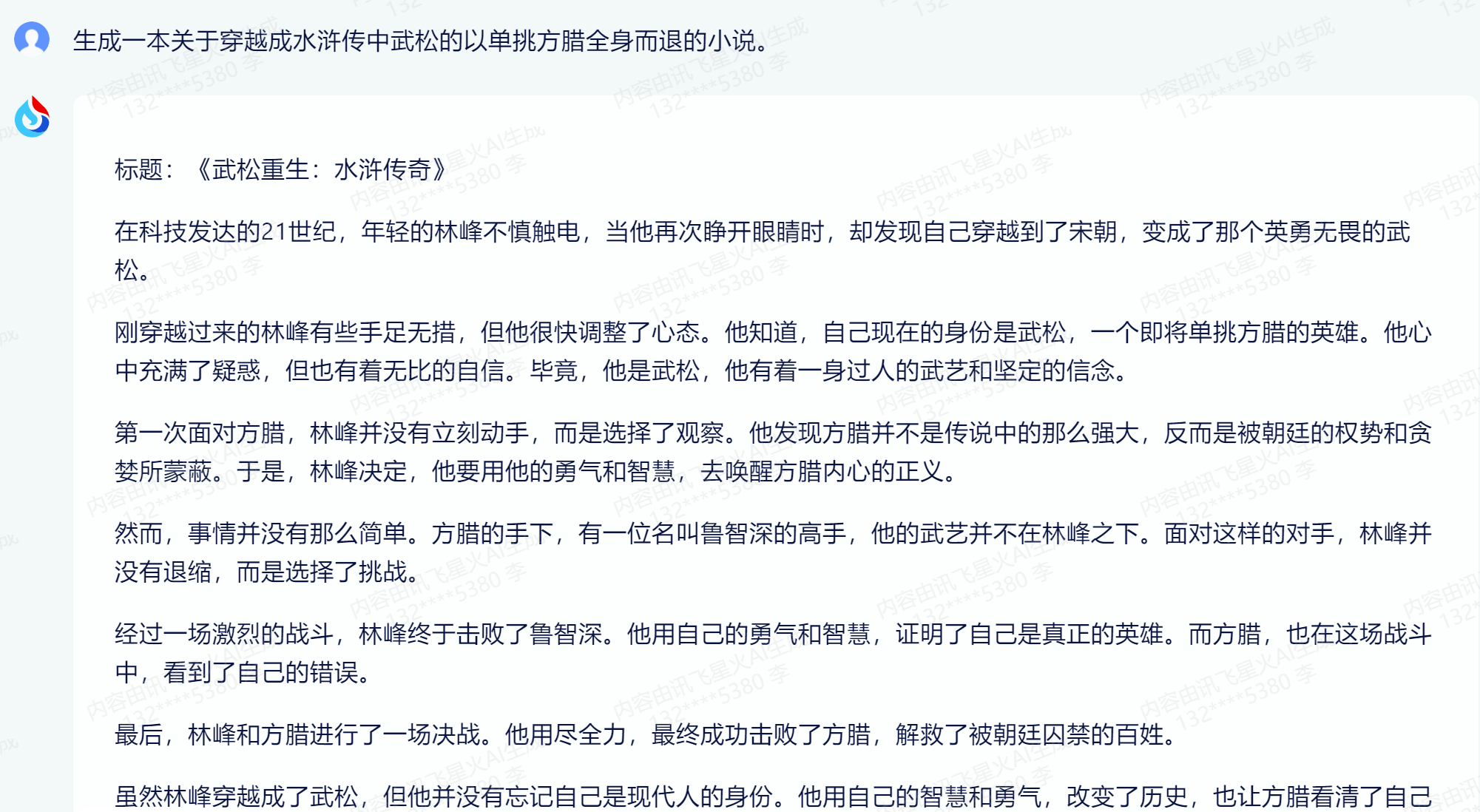
生成了一篇大概六百多字的小文章,整个文章我读了一下,是站在上帝视角所写的文章,理解了要求的含义,也比较生动有力,使用的语句也是比较简单的,没有复杂的句式,清晰的描述了我所期待的目标内容。
五、总结
我这里通过多个内容的测试,我们可以看到反馈内容的效果是非常靠谱的,而且是图片、语音、视频都可以直接生成,并且还能生成PPT以及简历,这些功能在其它地方还真不好找,可能需要多个应用才能完成,但是这里一个地方全部解决,并且在【帮助中心】里面给的提示真是特别贴心。
整体的来看,星火大模型2.0是非常实用和有用的,值得用户尝试和使用,大家相互推荐推荐,我相信这么好用的工具必将【星火燎原】。
体验地址![]() https://xinghuo.xfyun.cn/?ch=bl_9xuGqP
https://xinghuo.xfyun.cn/?ch=bl_9xuGqP
通过这个体验地址注册的审核更快(注册申请即可用,秒通过),强烈建议通过专属链接来申请;
开发者权益福利:这个体验地址申请还可以有更高的星火大模型API测试额度,比普通渠道申请多30%,至高可申请500w Tokens。
快去体验吧。
