广西旅游网站建设网站针对爬虫爬取做的优化
背景:公司有升级项目jdk的规划,计划从jdk8升级到jdk11
开始
首先配置本地的java_home
参考文档:Mac环境下切换JDK版本及不同的maven-CSDN博客
将pom.xml中jdk1.8相关的版本全部改为jdk17,主要是maven编译插件之类的,maven plugin也改为相应的支持jdk17的版本。
编译问题
[INFO] dmn-myproject .................................... SUCCESS [ 0.470 s]
[INFO] myproject-api .................................... SUCCESS [ 12.363 s]
[INFO] myproject-web .................................... FAILURE [ 20.003 s]
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD FAILURE
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 34.911 s
[INFO] Finished at: 2024-07-25T14:46:52+08:00
[INFO] Final Memory: 148M/534M
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[ERROR] Failed to execute goal org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-maven-plugin:2.3.12.RELEASE:repackage (repackage) on project myproject-web: Execution repackage of goal org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-maven-plugin:2.3.12.RELEASE:repackage failed: Unsupported class file major version 61 -> [Help 1]
[ERROR] <build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId><version>3.0.13</version><configuration><includeSystemScope>true</includeSystemScope></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><version>3.8.1</version><configuration><source>17</source><target>17</target></configuration></plugin></plugins></build>
改完以后这一步编译是正常通过的
[INFO] dmn-myproject .................................... SUCCESS [ 0.856 s]
[INFO] myproject-api .................................... SUCCESS [ 23.130 s]
[INFO] myproject-web .................................... SUCCESS [ 47.159 s]启动报如下错误
2024-07-24 13:12:41.243 [TID: N/A] ERROR 29462 --- [ main] o.s.boot.SpringApplication : Application run failedorg.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: Failed to read candidate component class: file [/Users/domino/IdeaProjects/dmn/dmn-myproject/myproject-web/target/classes/com/dmn/myproject/annotation/ResetPassword.class]; nested exception is org.springframework.core.NestedIOException: ASM ClassReader failed to parse class file - probably due to a new Java class file version that isn't supported yet: file [/Users/domino/IdeaProjects/dmn/dmn-myproject/myproject-web/target/classes/com/dmn/myproject/annotation/ResetPassword.class]; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Unsupported class file major version 61at org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.scanCandidateComponents(ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.java:452) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.findCandidateComponents(ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.java:315) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner.doScan(ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner.java:276) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScanAnnotationParser.parse(ComponentScanAnnotationParser.java:132) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClassParser.java:296) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClassParser.java:250) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.parse(ConfigurationClassParser.java:207) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.parse(ConfigurationClassParser.java:175) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.processConfigBeanDefinitions(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.java:320) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.java:237) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.java:280) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.java:96) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(AbstractApplicationContext.java:707) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:533) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.refresh(ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java:143) ~[spring-boot-2.3.12.RELEASE.jar:2.3.12.RELEASE]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh(SpringApplication.java:755) ~[spring-boot-2.3.12.RELEASE.jar:2.3.12.RELEASE]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh(SpringApplication.java:747) ~[spring-boot-2.3.12.RELEASE.jar:2.3.12.RELEASE]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext(SpringApplication.java:402) ~[spring-boot-2.3.12.RELEASE.jar:2.3.12.RELEASE]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:312) ~[spring-boot-2.3.12.RELEASE.jar:2.3.12.RELEASE]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1247) ~[spring-boot-2.3.12.RELEASE.jar:2.3.12.RELEASE]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1236) ~[spring-boot-2.3.12.RELEASE.jar:2.3.12.RELEASE]at com.dmn.myproject.PerformanceApplication.main(PerformanceApplication.java:26) ~[classes/:na]
Caused by: org.springframework.core.NestedIOException: ASM ClassReader failed to parse class file - probably due to a new Java class file version that isn't supported yet: file [/Users/domino/IdeaProjects/dmn/dmn-myproject/myproject-web/target/classes/com/dmn/myproject/annotation/ResetPassword.class]; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Unsupported class file major version 61at org.springframework.core.type.classreading.SimpleMetadataReader.getClassReader(SimpleMetadataReader.java:60) ~[spring-core-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.core.type.classreading.SimpleMetadataReader.<init>(SimpleMetadataReader.java:49) ~[spring-core-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.core.type.classreading.SimpleMetadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(SimpleMetadataReaderFactory.java:103) ~[spring-core-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.core.type.classreading.CachingMetadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(CachingMetadataReaderFactory.java:123) ~[spring-core-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.scanCandidateComponents(ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.java:429) ~[spring-context-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]... 21 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Unsupported class file major version 61at org.springframework.asm.ClassReader.<init>(ClassReader.java:196) ~[spring-core-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.asm.ClassReader.<init>(ClassReader.java:177) ~[spring-core-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.asm.ClassReader.<init>(ClassReader.java:163) ~[spring-core-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.asm.ClassReader.<init>(ClassReader.java:284) ~[spring-core-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]at org.springframework.core.type.classreading.SimpleMetadataReader.getClassReader(SimpleMetadataReader.java:57) ~[spring-core-5.2.15.RELEASE.jar:5.2.15.RELEASE]... 25 common frames omitted
需要升级springboot的相关版本,参考SpringBoot和JDK版本兼容性_jdk21 和 springboot 版本适配,最低可以从2.5.x开始,最高可以从3.0.x开始
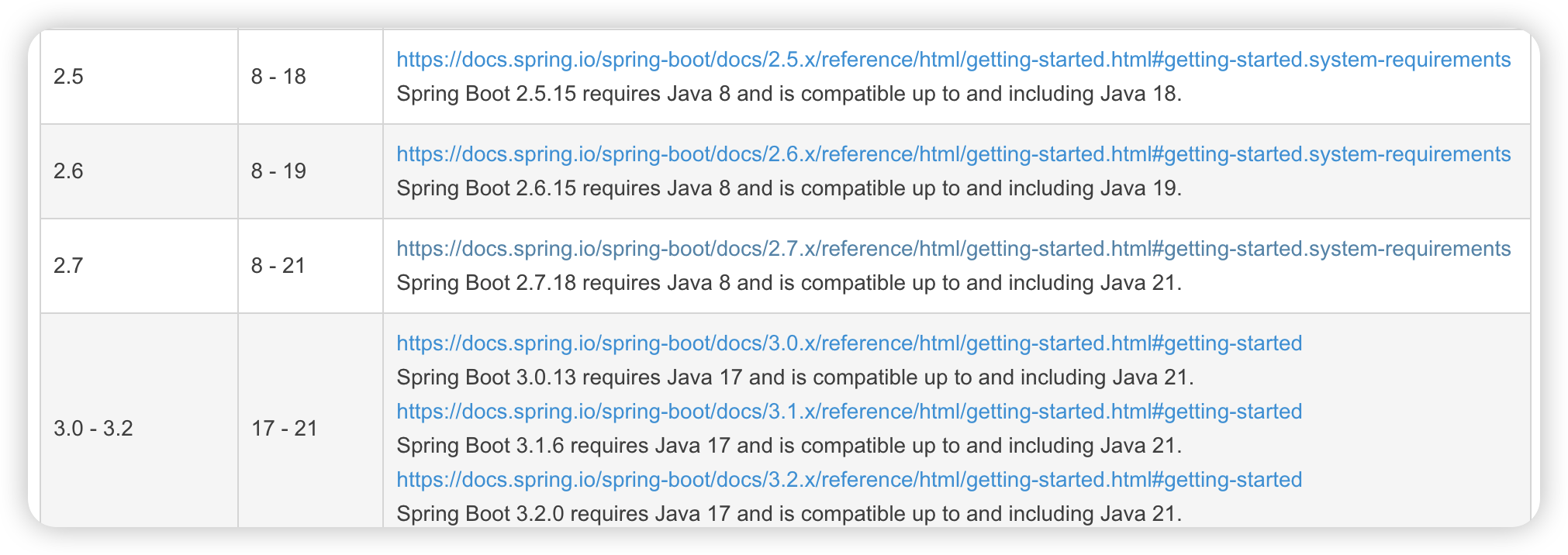
分别升级 springboot版本,spring版本, springcloud版本
springboot版本首先选择的是2.5.15,(优先选择符合版本,过高的版本会造成特别大的版本差异导致的问题,如tomcat的10以后的版本,升级以后,request影响的层面太大了,httpservletrequest全部需要变为 jarkata包下的,旧项目升级最好不要弄)
通过 mvn clean dependency:tree > a1.txt && open a1.txt
找到所有的org.springframework.boot相关的引用,将其版本改为2.5.15
(这里之所以要将所有的org.springframework.boot版本都进行替换增量的加到pom.xml文件中,原因有两方面,1,去每个引用下面排队其可能引用到的springboot、springcloud、spring依赖的工作量太大,而且因为引用了xxl-parent的缘故,里面定义的dependencyManagement会对当前项目引用的版本及相关的依赖的版本有影响,每项去找可能不全面
以下针对boot的处理对 spring及springcloud同理
)
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId><version>${springboot.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId><version>${springboot.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>${springboot.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId><version>${springboot.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId><version>${springboot.version}</version></dependency>
再将 所有的org.springframework相关的引用,版本改为与springboot对应的5.3.27
Spring Boot 2.5.15 requires [Java 8](https://www.java.com/) and is compatible up to and including Java 18. [Spring Framework 5.3.27](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.3.27/reference/html/) or above is also required.
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-web</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-core</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-jcl</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version></dependency>
springcloud的版本先不改,先用当前版本启动试试看,不改不一定有影响
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId><version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter</artifactId><version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-context</artifactId><version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-openfeign-core</artifactId><version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-netflix-ribbon</artifactId><version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-netflix-archaius</artifactId><version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-commons</artifactId><version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version></dependency>
启动后报如下错: 说明与springcloud版本有关,还是要升级
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'configurationPropertiesBeans' defined in class path resource [org/springframework/cloud/autoconfigure/ConfigurationPropertiesRebinderAutoConfiguration.class]: Post-processing of merged bean definition failed; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to introspect Class [org.springframework.cloud.context.properties.ConfigurationPropertiesBeans] from ClassLoader [jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@251a69d7]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:597) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:542) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.lambda$doGetBean$0(AbstractBeanFactory.java:335) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:234) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:333) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:213) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.java:270) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.registerBeanPostProcessors(AbstractApplicationContext.java:764) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:567) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh(SpringApplication.java:745) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext(SpringApplication.java:423) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:307) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder.run(SpringApplicationBuilder.java:164) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener.bootstrapServiceContext(BootstrapApplicationListener.java:212) ~[spring-cloud-context-2.2.9.RELEASE.jar:2.2.9.RELEASE]at org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener.onApplicationEvent(BootstrapApplicationListener.java:117) ~[spring-cloud-context-2.2.9.RELEASE.jar:2.2.9.RELEASE]at org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener.onApplicationEvent(BootstrapApplicationListener.java:74) ~[spring-cloud-context-2.2.9.RELEASE.jar:2.2.9.RELEASE]at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.doInvokeListener(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:176) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.invokeListener(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:169) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:143) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:131) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener.environmentPrepared(EventPublishingRunListener.java:85) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners.lambda$environmentPrepared$2(SpringApplicationRunListeners.java:66) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at java.base/java.util.ArrayList.forEach(ArrayList.java:1511) ~[na:na]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners.doWithListeners(SpringApplicationRunListeners.java:120) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners.doWithListeners(SpringApplicationRunListeners.java:114) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners.environmentPrepared(SpringApplicationRunListeners.java:65) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.prepareEnvironment(SpringApplication.java:343) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:301) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1317) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1306) ~[spring-boot-2.6.15.jar:2.6.15]at com.dmn.myproject.PerformanceApplication.main(PerformanceApplication.java:26) ~[classes/:na]
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to introspect Class [org.springframework.cloud.context.properties.ConfigurationPropertiesBeans] from ClassLoader [jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@251a69d7]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:485) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:321) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.buildLifecycleMetadata(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:232) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.findLifecycleMetadata(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:210) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:149) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:305) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1116) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:594) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]... 30 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/springframework/boot/context/properties/ConfigurationBeanFactoryMetadataat java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods0(Native Method) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.privateGetDeclaredMethods(Class.java:3402) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods(Class.java:2504) ~[na:na]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:467) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]... 37 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationBeanFactoryMetadataat java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:641) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:188) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:520) ~[na:na]... 41 common frames omittedspringcloud版本来自
Spring Cloud 2021.0 Release Notes · spring-cloud/spring-cloud-release Wiki (github.com)
<!-- springcloud --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId><version>${springcloud.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter</artifactId><version>${springcloud.version.jdk17}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-openfeign-core</artifactId><version>${springcloud.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-context</artifactId><version>${springcloud.version.jdk17}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-commons</artifactId><version>${springcloud.version.jdk17}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon</artifactId><version>${springcloud.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-netflix-ribbon</artifactId><version>${springcloud.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-netflix-archaius</artifactId><version>${springcloud.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-archaius</artifactId><version>${springcloud.version}</version></dependency>
再次启动报如下错误错
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Error processing condition on org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.data.RepositoryMetricsAutoConfiguration.metricsRepositoryMethodInvocationListenerat org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.SpringBootCondition.matches(SpringBootCondition.java:60) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(ConditionEvaluator.java:108) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.java:193) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.java:153) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.java:129) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.processConfigBeanDefinitions(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.java:343) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.java:247) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.java:311) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.java:112) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(AbstractApplicationContext.java:748) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:564) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.refresh(ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java:145) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh(SpringApplication.java:780) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext(SpringApplication.java:453) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:343) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1370) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1359) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at com.dmn.myproject.PerformanceApplication.main(PerformanceApplication.java:26) ~[classes/:na]
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: @ConditionalOnMissingBean did not specify a bean using type, name or annotation and the attempt to deduce the bean's type failedat org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition$Spec.validate(OnBeanCondition.java:494) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition$Spec.<init>(OnBeanCondition.java:443) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition.getMatchOutcome(OnBeanCondition.java:154) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.SpringBootCondition.matches(SpringBootCondition.java:47) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]... 17 common frames omitted
Caused by: org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition$BeanTypeDeductionException: Failed to deduce bean type for org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.data.RepositoryMetricsAutoConfiguration.metricsRepositoryMethodInvocationListenerat org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition$Spec.deducedBeanTypeForBeanMethod(OnBeanCondition.java:524) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition$Spec.deducedBeanType(OnBeanCondition.java:513) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition$Spec.<init>(OnBeanCondition.java:436) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]... 19 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/springframework/data/repository/core/support/RepositoryMethodInvocationListenerat java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass1(Native Method) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass(ClassLoader.java:1012) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.security.SecureClassLoader.defineClass(SecureClassLoader.java:150) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.defineClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:862) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.findClassOnClassPathOrNull(BuiltinClassLoader.java:760) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClassOrNull(BuiltinClassLoader.java:681) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:639) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:188) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:520) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName0(Native Method) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName(Class.java:467) ~[na:na]at org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition.resolve(FilteringSpringBootCondition.java:108) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition$Spec.getReturnType(OnBeanCondition.java:532) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition$Spec.deducedBeanTypeForBeanMethod(OnBeanCondition.java:520) ~[spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]... 21 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.springframework.data.repository.core.support.RepositoryMethodInvocationListenerat java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:641) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:188) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:520) ~[na:na]... 35 common frames omitted2024-07-25 16:29:57.769 [TID: N/A] WARN 69947 --- [ main] o.s.boot.SpringApplication : Unable to close ApplicationContextjava.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to introspect Class [org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.data.RepositoryMetricsAutoConfiguration] from ClassLoader [jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@251a69d7]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:485) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:361) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getUniqueDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:418) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.lambda$getTypeForFactoryMethod$2(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:765) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap.computeIfAbsent(ConcurrentHashMap.java:1708) ~[na:na]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.getTypeForFactoryMethod(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:764) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.determineTargetType(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:703) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.predictBeanType(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:674) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.isFactoryBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:1684) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.doGetBeanNamesForType(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:570) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:542) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBeansOfType(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:669) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBeansOfType(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:661) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBeansOfType(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1302) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.getExitCodeFromMappedException(SpringApplication.java:913) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.getExitCodeFromException(SpringApplication.java:901) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.handleExitCode(SpringApplication.java:888) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.handleRunFailure(SpringApplication.java:828) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:353) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1370) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1359) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at com.dmn.myproject.PerformanceApplication.main(PerformanceApplication.java:26) ~[classes/:na]
Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/springframework/data/repository/core/support/RepositoryMethodInvocationListenerat java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass1(Native Method) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass(ClassLoader.java:1012) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.security.SecureClassLoader.defineClass(SecureClassLoader.java:150) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.defineClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:862) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.findClassOnClassPathOrNull(BuiltinClassLoader.java:760) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClassOrNull(BuiltinClassLoader.java:681) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:639) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:188) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:520) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods0(Native Method) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.privateGetDeclaredMethods(Class.java:3402) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods(Class.java:2504) ~[na:na]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:467) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]... 21 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.springframework.data.repository.core.support.RepositoryMethodInvocationListenerat java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:641) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:188) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:520) ~[na:na]... 34 common frames omitted
以上通过错误排查,应该是org.springframework.data 相关的包有问题,通过 mvn clean dependency:tree > a1.txt && open a1.txt看到与data有关的包如下,全部进行升级
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb:jar:2.5.15:compile
[INFO] | +- org.mongodb:mongodb-driver-sync:jar:4.0.6:compile
[INFO] | | +- org.mongodb:bson:jar:4.0.6:compile
[INFO] | | \- org.mongodb:mongodb-driver-core:jar:4.0.6:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework.data:spring-data-mongodb:jar:3.0.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework.data:spring-data-commons:jar:2.3.9.RELEASE:compile
。。。省略。。。
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-redis:jar:2.5.15:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework.data:spring-data-redis:jar:2.3.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | \- org.springframework.data:spring-data-keyvalue:jar:2.3.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | \- io.lettuce:lettuce-core:jar:5.3.7.RELEASE:compileorg.springframework.data:spring-data-mongodb:jar:3.0.9.RELEASE:compile
org.springframework.data:spring-data-commons:jar:2.3.9.RELEASE:compile
org.springframework.data:spring-data-redis:jar:2.3.9.RELEASE:compile
org.springframework.data:spring-data-keyvalue:jar:2.3.9.RELEASE:compile分别到其顶级的starter中找到其适配的版本。(这里之所以spring-boot-starter-data-redis版本是2.5.15,但是其依赖的spring-data-redis版本是2.3.9.RELEASE而不是starter中对应的2.5.12,原因就是受到 xxl-parent中依赖版本定义的影响)<!-- springdata --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId><artifactId>spring-data-commons</artifactId><version>${springdata.commons}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId><artifactId>spring-data-mongodb</artifactId><version>${springdata.mongodb}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId><artifactId>spring-data-keyvalue</artifactId><version>${springdata.keyvalue}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId><artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId><version>${springdata.redis}</version></dependency>
以下为遇到的其他的版本相关的问题:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to introspect Class [org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.mongo.MongoMetricsAutoConfiguration$MongoConnectionPoolMetricsConfiguration] from ClassLoader [jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@251a69d7]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:485) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:361) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getUniqueDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:418) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.lambda$getTypeForFactoryMethod$2(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:765) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap.computeIfAbsent(ConcurrentHashMap.java:1708) ~[na:na]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.getTypeForFactoryMethod(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:764) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.determineTargetType(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:703) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.predictBeanType(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:674) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.isFactoryBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:1684) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.doGetBeanNamesForType(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:570) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:542) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBeansOfType(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:669) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBeansOfType(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:661) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBeansOfType(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1302) ~[spring-context-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.getExitCodeFromMappedException(SpringApplication.java:913) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.getExitCodeFromException(SpringApplication.java:901) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.handleExitCode(SpringApplication.java:888) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.handleRunFailure(SpringApplication.java:828) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:353) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1370) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1359) ~[spring-boot-2.5.15.jar:2.5.15]at com.dmn.myproject.PerformanceApplication.main(PerformanceApplication.java:26) ~[classes/:na]
Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: io/micrometer/core/instrument/binder/mongodb/MongoConnectionPoolTagsProviderat java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods0(Native Method) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.privateGetDeclaredMethods(Class.java:3402) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods(Class.java:2504) ~[na:na]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:467) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]... 21 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: io.micrometer.core.instrument.binder.mongodb.MongoConnectionPoolTagsProviderat java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:641) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:188) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:520) ~[na:na]... 25 common frames omitted找到关键字,在tree信息中找到包名,在starter中找到版本
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator:jar:2.5.15:compile
[INFO] | \- io.micrometer:micrometer-core:jar:1.5.14:compile
[INFO] | \- org.latencyutils:LatencyUtils:jar:2.0.3:runtime
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to introspect Class [org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitProperties] from ClassLoader [jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@251a69d7]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:485) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:321) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.determineCandidateConstructors(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:267) ~[spring-beans-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]... 88 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/springframework/amqp/rabbit/connection/AbstractConnectionFactory$AddressShuffleModeat java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods0(Native Method) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.privateGetDeclaredMethods(Class.java:3402) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods(Class.java:2504) ~[na:na]at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.getDeclaredMethods(ReflectionUtils.java:467) ~[spring-core-5.3.27.jar:5.3.27]... 90 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.AbstractConnectionFactory$AddressShuffleModeat java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:641) ~[na:na]at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:188) ~[na:na]at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:520) ~[na:na]... 94 common frames omitted与amqp有关,升级amqp相关包
org.springframework.amqp:spring-rabbit:jar:2.2.18.RELEASE:compile
org.springframework.amqp:spring-amqp:jar:2.2.18.RELEASE:compile[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-amqp:jar:2.5.15:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework.amqp:spring-rabbit:jar:2.2.18.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- com.rabbitmq:amqp-client:jar:5.9.0:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework.amqp:spring-amqp:jar:2.2.18.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework.retry:spring-retry:jar:1.2.5.RELEASE:compile参考文档
Spring Cloud
springcloud与springboot对应版本
Spring Cloud 2022.0 Release Notes · spring-cloud/spring-cloud-release Wiki (github.com)
springcloud版本对应的下级版本
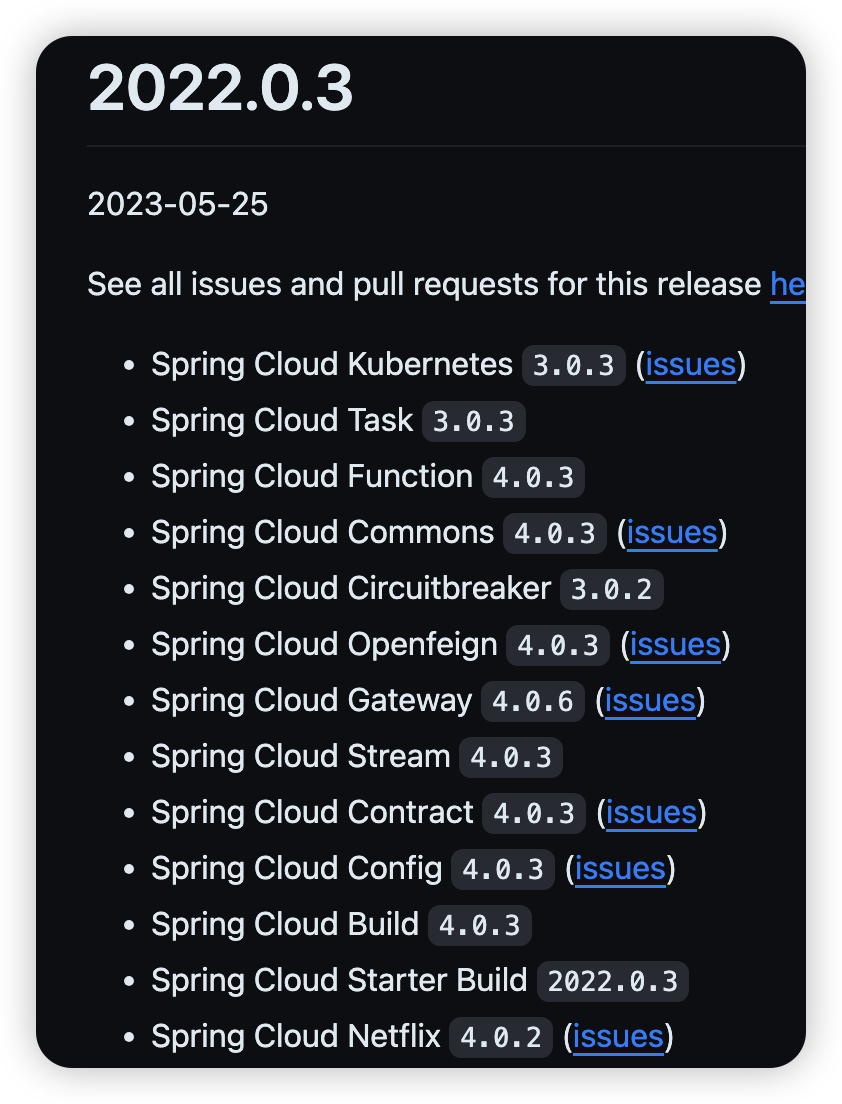
如何查看springboot依赖的jdk版本 如何查看springboot依赖的JDK版本
