网页制作企业网站作业检察机关门户网站建设情况
有问题别自己克服,来抖音电商找“达人客服”
当代年轻人购物,正在从机智省变成理智购。越来越多的人在达人直播间购物,看重的不止是优惠力度,还有服务保障。
为了帮助达人更好地服务用户,抖音电商上线了「达人客服」功能,在「商家客服」和「平台客服」之外,用户还可以通过达人自有的客服团队,进行电商带货场景的问题反馈和在线咨询,达人团队工作人员将会出面联系商家、物流等,提供一站式解决方案和一条龙服务。
用户找到「达人客服」入口的具体操作方式如下:
直播时段:点击直播间购物车,右上角点击“达人客服”图标,即可开启聊天对话
非直播时段:点击达人主页,进入商品橱窗,右上角点击“达人客服”图标,即可开启聊天对话
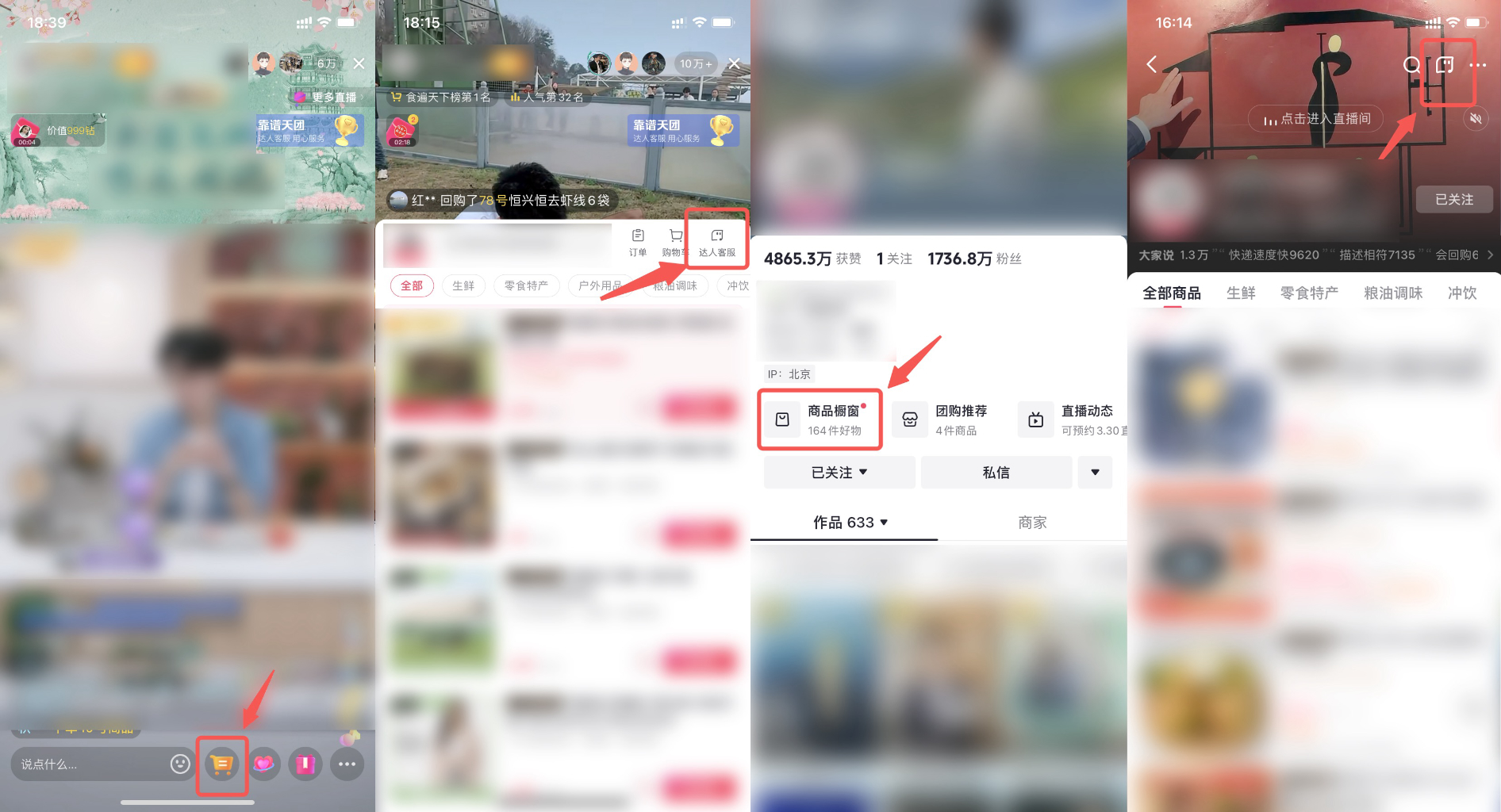
图一:直播时段
图二:非直播时段
达人客服,更懂达人团队所需的用户服务工具
在为消费者提供更好服务、更多保障的同时,「达人客服」也同样能够帮助达人团队提高工作效率。
相比于私信,针对「达人客服」功能,平台配套了达人授权机构接待客服咨询、子账号客服接待授权、商达协同任务单、小额打款等辅助功能点,可以协助达人通过更完善的客服工具,打造更独立/更专业的达人客服团队心智,为粉丝进行商品、物流、售后等问题的高效处理,保障消费咨询体验。
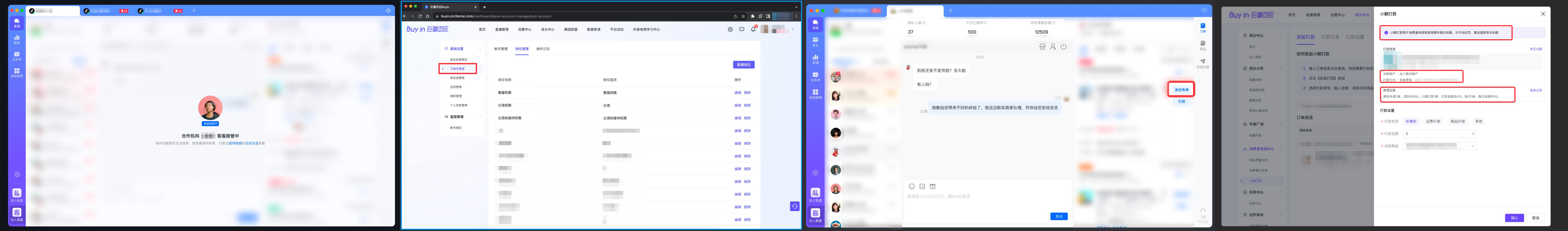
图一:达人授权机构接待客服咨询
图二:子账号客服接待授权
图三:商达协同任务单
图四:小额打款
目前,达人团队可以通过三种方式进入达人客服,进行客服接待:
1)登录百应后台 → 点击右上角用户客服消息 → 进入达人客服 → 进行达人客服接待;
2)下载达人客服PC桌面端(https://darenim.jinritemai.com/v2/daren_download) → 根据登录账号类型选择「飞鸽·达人版」或「飞鸽·机构版」 → 进行达人客服接待;
3)登录抖音APP → 进入我的主页 → 商品橱窗 → 点击右上角的客服接待 → 进行达人客服接待(暂仅支持达人主账号登录)。
众多明星头达率先使用,邀请用户“321上客服”
“达人客服”产品功能上线后,众多明星头达率先开通使用,@与辉同行 、@郝劭文 、@李晨nic 、@刘媛媛 、@朱梓骁 携团队幕后伙伴出镜,同大家分享“服务宣言”。

为了便于粉丝更快找到“达人客服”入口,“靠谱天团”成员们精心策划制作讲解短视频,并通过直播间互动等形式,集体喊话粉丝“有问题别自己克服,来找我们的达人客服”,引导粉丝了解并找到咨询入口。

仅需两步,快速为团队开启“达人客服”功能
看了这么多,是不是想知道抖音电商“达人客服”到底怎么开通?别急,仅需两步,即可快速启用!
Step1:账号权限配置 (若直接使用主账号接待可跳过此步)
登录百应后台 → 设置 → 子账号设置 → 开通"达人客服接待"权限
Step2:登录达人客服开启接待(三种方式可选,首次建议使用主账号登录,之后再用子账号进行日常登录)
通过百应后台 → 用户客服消息 → 切换"在线"状态开启接待
下载飞鸽桌面端 → 登录飞鸽达人版或机构版 → 切换"在线"状态开启接待
登录抖音APP → 我的主页 → 商品橱窗 → 右上角的客服接待 → 切接"在线"状态开启接待(仅限主账号)
进阶版操作详情,可以往下看:
场景一:达人账号自主配置客服接待
如果达人有自己的客服团队,只要安装飞鸽-达人版客户端,开通并登录账号,就可以了!
如需使用其他子账号进行客服接待,也可以通过达人主账号登录巨量百应客户端,单独配置客服子账号,具体流程如下:
(1)进入百应达人后台,点击右上角“设置 → 子账号设置”;
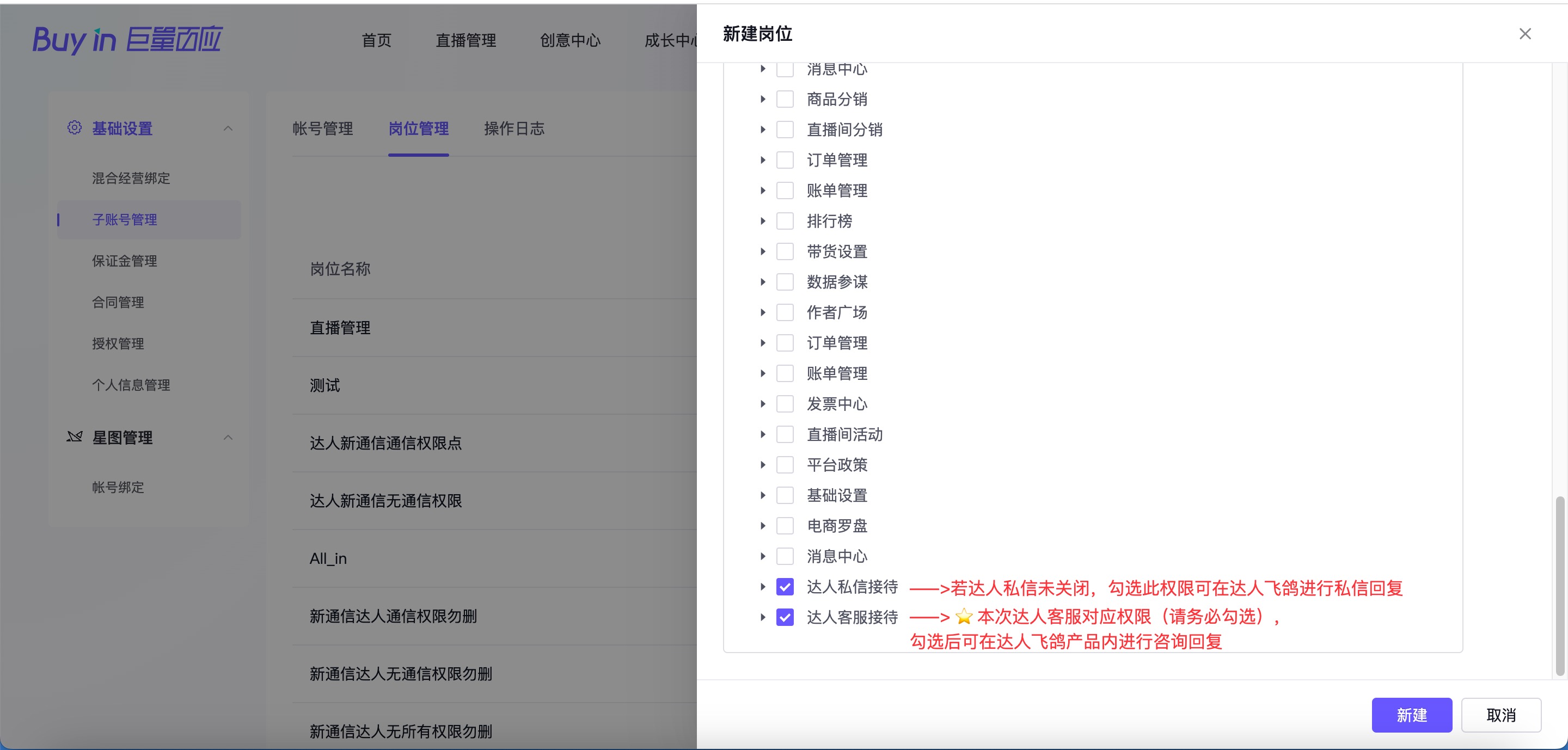
(2)点击“新建岗位”,进行子账号权限配置;
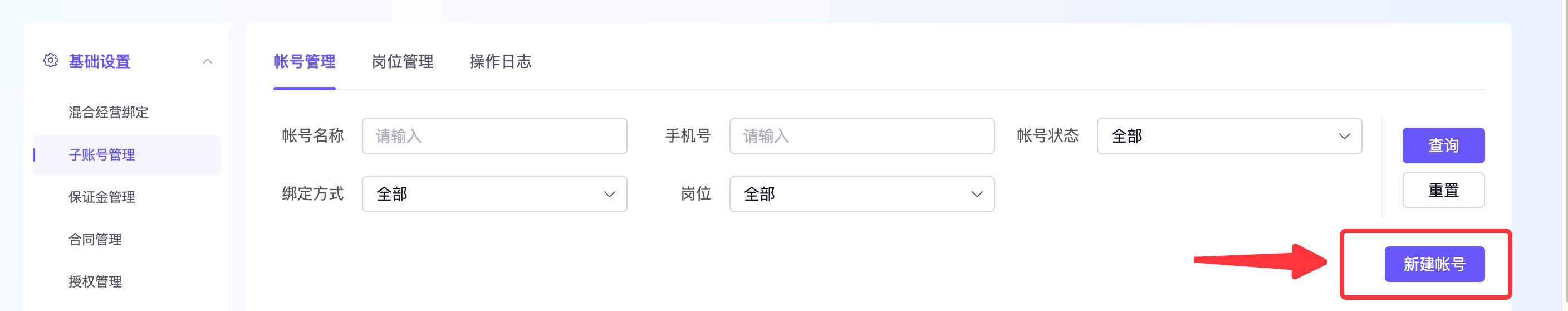
(3)点击“新建账号”,给具体子账号关联带上达人客服接待权限的岗位。
图一:百应后台 → 设置 → 子账号设置
图二:新建岗位 → 新建账号
图三:主管性质子账号权限建议
图四:接待客服子账号权限建议
需要注意的是,“达人客服”和现有“达人私信”共用一个消息提醒和入口,当私信和达人客服同时有消息时,会优先进入达人客服接待页面哦!

百应后台 → 设置 → 子账号设置
新建岗位 → 新建账号

主管性质子账号权限建议

接待客服子账号权限建议
场景二:达人授权机构进行客服接待
如果达人希望和机构合作,共同运营客服团队,那么可按如下流程操作:
流程①:机构安装「飞鸽·机构版」客户端后,开通并登录账号,向有绑定关系的达人发起接待接管。
流程②:达人同意后,接管生效,达人不能再回复消息,但可以查看历史会话,如遇到达人无法同意的情况,可能是因为还有未关闭的会话,记得先点击关闭全部会话,再确认同意哦!同时,达人无需征求合作机构同意,也可以随时主动关闭接管状态。
流程③:同意接管后,达人的用户进线全部由机构接待,同时也可以在历史会话中区分达人客服接待和机构客服接待,更方便用户会话管理!

综上,抖音电商“达人客服”功能开通攻略已介绍完毕。
期待越来越多的主播团队通过达人客服,为粉丝带去更好的购物体验!
了解更多【达人服务】达人客服产品开通和操作指南点击链接:https://bytedance.larkoffice.com/docx/JkZAdy6zEoIZyhxkb4CctliqnEd
