收费网站必须备案吗wordpress加载js代码
目录
Pinia状态管理库
使用步骤
1、安装Pinia
2、在vue应用实例中使用pinia
3、在src/stores/token.js中定义stores
4、在组件中使用store
axios请求拦截器
代码实现
Pinia状态管理库
Pinia是Vue的专属状态管理库,它允许你跨组件或页面共享状态
一般在登录时会产生一个token,在访问其他接口的时候要携带这个token才能成功访问。我们使用测试工具postman测试的时候可以直接在Header中携带token,但是我们在之前在学习vue的时候使用axios直接就访问了接口,这样除非是后端没有编写拦截器,否则是无法访问的。为了解决这个问题,让我们浏览器也可以成功访问拦截器生效的接口,我们就要使用到Pinia了。
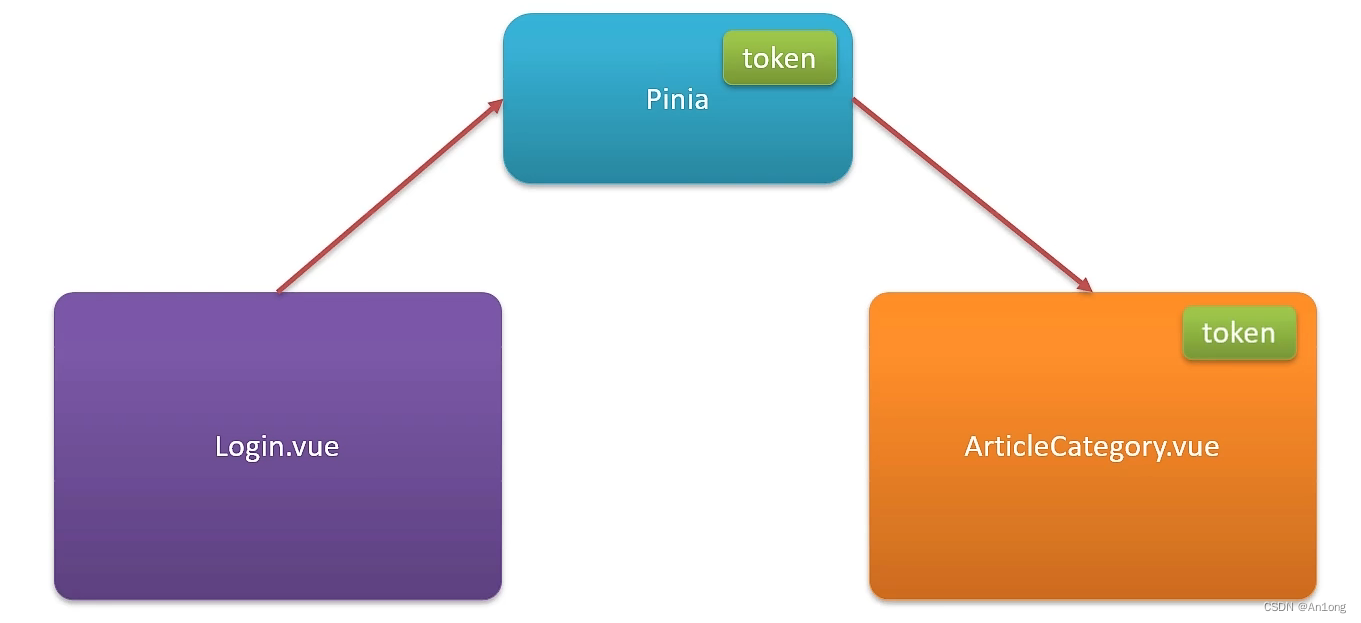
你可以将pinia简单的理解为中转站,能让一个组件使用到另一个组件的东西
使用步骤
1、安装Pinia
在项目命令行下安装Pinia,指令:npm install pinia

2、在vue应用实例中使用pinia

3、在src/stores/token.js中定义stores

这里使用const定义了token,但这并不代表它的值不可以改变了。const不可改变的是它的引用地址。在这个例子中, const token = ref(' ')中的token是一个引用变量,而不是原始值。这意味着你可以通过token,value来改变引用变量的值。
4、在组件中使用store

如:
在登录时将生成的token放入生成的tokenStore中
//获取登录生成的token
import {useTokenStore} from '@/stores/token.js'
const tokenStore = useTokenStore();//登陆接口
const login = async function(){let result = await userLoginService(registerData.value);ElMessage.success("登录成功");//将获取生成的token存储到pinia中tokenStore.setToken(result.data)router.push('/')
}然后在需要使用token验证的接口哪里从存储的store中取出来,赋值给响应头heanders就携带了token了
import request from '@/utils/request.js'
import {useTokenStore} from '@/stores/token.js'export const categoryListService = function(){const tokenStore = useTokenStore();// tokenStore.token就是token//在pinia中定义的响应式数据都不需要加上.valuereturn request.get('/category/list',{headers:{'Authorization':tokenStore.token}})
}axios请求拦截器
像上面的例子中,一个接口使用到token 就要方法里写调用tokenStore,然后再headers上加token。如果一堆接口都要使用,那么每一个接口中都要写这个一摸一样的逻辑,复用性极强。为了偷懒也为了代码的整洁美观,复用性高的代码片段我们想办法只写一次一劳永逸。为此要使用到请求拦截器,每次发起请求,直接拦截下来然后自动给你安上token。

这个请求拦截器和我们之前学的响应拦截器很相似,只不过是没了result回调函数,取而代之的是一个config回调函数,这里面就是用在写在发起请求之前拦截下来做些什么。
代码实现
//定制请求的实例//导入axios npm install axios
import axios from 'axios';
import { ElMessage } from 'element-plus';//导入定义好的状态
import { useTokenStore } from '@/stores/token.js';//定义一个变量,记录公共的前缀 , baseURL
const baseURL = '/api'
const instance = axios.create({baseURL})//添加请求拦截器
instance.interceptors.request.use(config => {//添加tokenconst tokenStore = useTokenStore();if(tokenStore.token){config.headers.Authorization = tokenStore.token;}return config;},err => {ElMessage.error('请求异常');return Promise.reject(err);//异步的状态转化成失败的状态}
)//添加响应拦截器
instance.interceptors.response.use(result => {if(result.data.code == 0){return result.data;}else{ElMessage.error(result.data.message ? result.data.message : '服务异常')//结束异步操作return Promise.reject(result.data);}},err => {ElMessage.error(result.data.message ? result.data.message : '服务异常');return Promise.reject(err);//异步的状态转化成失败的状态}
)export default instance;
注意:如果出现这个错误,不是代码的问题,是token过期了,重新登录一下就可以了
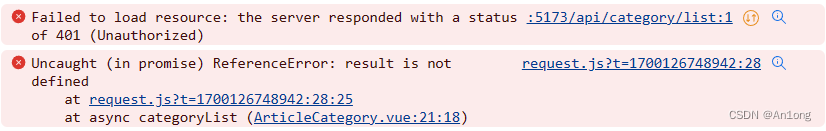
Pinia问题解决 - 补充
Pinia持久化插件 - perisist
使用pinia的时候会遇到一个bug,本来已经登录了,数据也显示出来了,但是当你刷新页面之后,又请求异常了
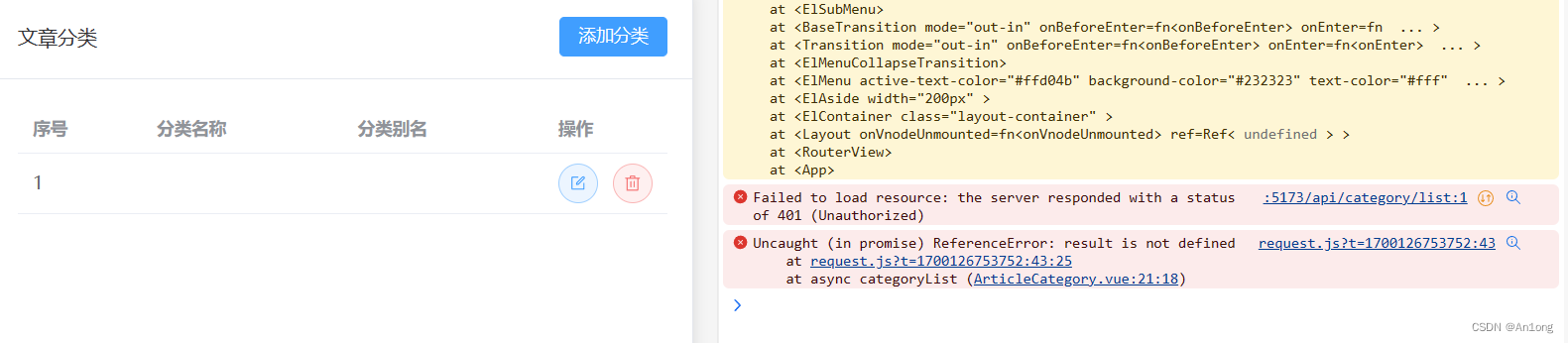
这是因为Pinia默认是内存存储,刷新浏览器的就会丢失数据,因此要使用Persist插件可以将pinia中的数据持久化的存储
使用方法
- 安装persist:npm install pinia-persistedstate-plugin

- 在pinia中使用persist

与其他不同,不是app使用,而是pinia使用
- 定义状态Store时指定持久化配置参数
//定义store
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
import {ref} from 'vue'//第一个参数:名字,唯一性
//第二个参数:函数的内部可以定义状态的所有内容//返回值:函数export const useTokenStore = defineStore('token',()=>{const token = ref('')const setToken = (newToken) =>{token.value = newToken;}const removeToken = () => {token.value=''}return {token,setToken,removeToken}
},{persist:true //开启持久化存储
});在使用token的这个地方使用persist:true开启持久化存储
这样刷新页面之后,pinia中存储的数据也不会消失了
未登录统一处理
现在使用的edge浏览器访问的接口,现在我们直接复制地址,用另一个浏览器打开
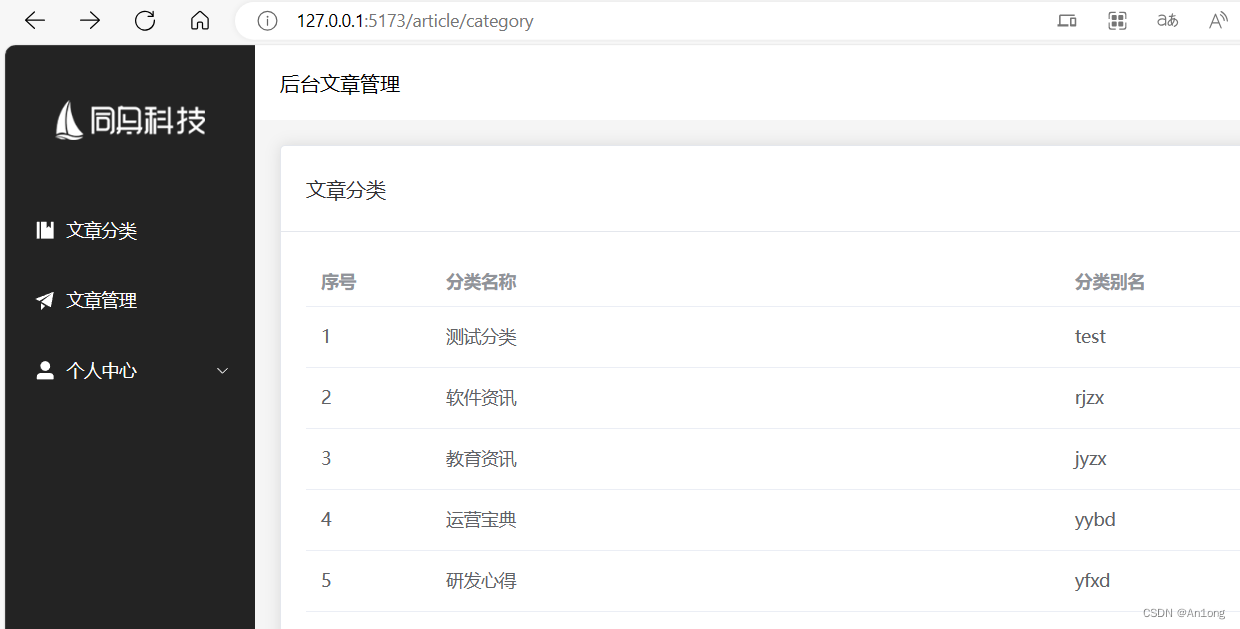
使用Chrome浏览器打开这个地址,我们发现还是停留在这个界面
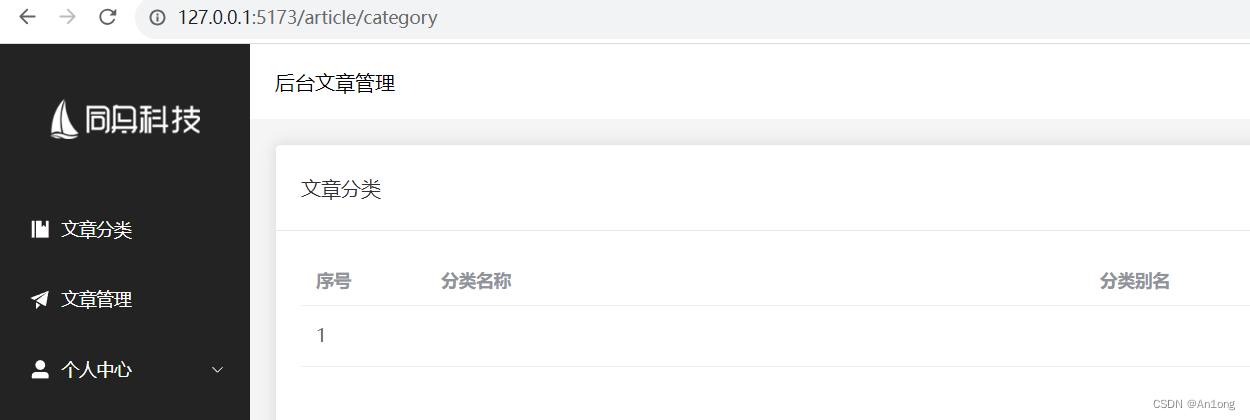
当我们访问这个地址的时候,由于在这个浏览器中没有登录过,也就没有token。我们所希望的是可以直接跳转到登录注册界面,让用户去登录生成token,总不能让用户自己在地址栏手动输入/login的url吧。
响应拦截器是检查是否携带token的,因此我们要在这里做判断,判断是否为登录状态,如果不是,那么就重定向至登录界面
import router from '@/router'//添加响应拦截器
instance.interceptors.response.use(result => {if(result.data.code == 0){return result.data;}else{ElMessage.error(result.data.message ? result.data.message : '服务异常')//结束异步操作return Promise.reject(result.data);}},err => {if(err.response.status === 401){ElMessage.error("请先登录");router.push('/login')}else{ElMessage.error(result.data.message ? result.data.message : '服务异常');}return Promise.reject(err);//异步的状态转化成失败的状态}