查询网站是否正规商贸有限公司起名
文章目录
- u-boot 编译与运行
- 环境配置
- ubuntu 版本
- qemu 版本
- u-boot 版本(master)
- 交叉工具链版本
- u-boot 源码下载
- 生成配置文件
- 报错情况一
- 报错情况2
- u-boot 配置
- 编译
- 编译脚本
- 编译报错解决
- 编译日志
- 编译产物
- 运行
u-boot 编译与运行
本文主要介绍 u-boot 编译,以及 qemu 如何运行 u-boot
环境配置
ubuntu 版本
tyustli@tyustli-machine:~/code/open_source/u-boot$ uname -a
Linux tyustli-machine 6.2.0-34-generic #34~22.04.1-Ubuntu SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Thu Sep 7 13:12:03 UTC 2 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
qemu 版本
tyustli@tyustli-machine:~/code/open_source/u-boot$ qemu-img -V
qemu-img version 6.2.0 (Debian 1:6.2+dfsg-2ubuntu6.11)
Copyright (c) 2003-2021 Fabrice Bellard and the QEMU Project developers
u-boot 版本(master)
commit 997bef3c6d22d12c7fd092fb831bf94d114c9f6f (HEAD -> master, origin/master, origin/HEAD)=> version
U-Boot 2023.10-00813-g997bef3c6d (Oct 12 2023 - 21:45:33 +0800)arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-gcc (GNU Toolchain for the A-profile Architecture 10.3-2021.07 (arm-10.29)) 10.3.1 20210621
GNU ld (GNU Toolchain for the A-profile Architecture 10.3-2021.07 (arm-10.29)) 2.36.1.20210621
交叉工具链版本
tyustli@tyustli-machine:~/code/open_source/u-boot$ arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -v
Using built-in specs.
COLLECT_GCC=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-gcc
COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/home/tyustli/cross_tool/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin/../libexec/gcc/arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/10.3.1/lto-wrapper
Target: arm-none-linux-gnueabihf
Configured with: /data/jenkins/workspace/GNU-toolchain/arm-10/src/gcc/configure --target=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf --prefix= --with-sysroot=/arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/libc --with-build-sysroot=/data/jenkins/workspace/GNU-toolchain/arm-10/build-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/install//arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/libc --with-bugurl=https://bugs.linaro.org/ --enable-gnu-indirect-function --enable-shared --disable-libssp --disable-libmudflap --enable-checking=release --enable-languages=c,c++,fortran --with-gmp=/data/jenkins/workspace/GNU-toolchain/arm-10/build-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/host-tools --with-mpfr=/data/jenkins/workspace/GNU-toolchain/arm-10/build-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/host-tools --with-mpc=/data/jenkins/workspace/GNU-toolchain/arm-10/build-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/host-tools --with-isl=/data/jenkins/workspace/GNU-toolchain/arm-10/build-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/host-tools --with-arch=armv7-a --with-fpu=neon --with-float=hard --with-mode=thumb --with-arch=armv7-a --with-pkgversion='GNU Toolchain for the A-profile Architecture 10.3-2021.07 (arm-10.29)'
Thread model: posix
Supported LTO compression algorithms: zlib
gcc version 10.3.1 20210621 (GNU Toolchain for the A-profile Architecture 10.3-2021.07 (arm-10.29))
u-boot 源码下载
u-boot 官网:https://source.denx.de/u-boot/u-boot,可以直接下载 master
git clone https://source.denx.de/u-boot/u-boot.git
生成配置文件
sudo make vexpress_ca9x4_defconfig ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-
u-boot 支持的板子可以使用如下命令
ls ./configs
此时会报错
/bin/sh: 1: arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-gcc: not found
此时分两种情况
报错情况一
如果安装了交叉编译工具链,通过命令行 arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc -v 可以显示出版本,如下所示。此时如果使用普通用户 sudo make ,则会出现以上所说错误。
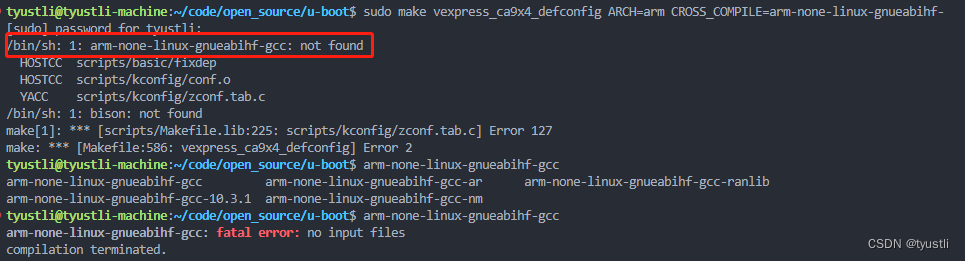
- 原因:使用普通用户下编译,可能是因为权限不足导致
- 解决方法:只需切换为 root 用户编译就可以通过,输入:su [密码]
输入 su 又会报错
su: Authentication failure
这个问题产生的原因是由于ubtun系统默认是没有激活root用户的,需要我们手工进行操作,在命令行界面下,或者在终端中输入如下命令:
sudo passwd
Password:你当前的密码Enter new UNIX password:这个是root的密码
Retype new UNIX password:重复root的密码
然后会提示成功的信息。
说明一点,使用su和sudo是有区别的,使用su切换用户需要输入所切换到的用户的密码,而使用sudo则是当前用户的密码。
切换用户的命令是su,su是(switch user)切换用户的缩写。通过su命令,可以从普通用户切换到root用户,也可以从root用户切换到普通用户。从普通用户切换到root用户需要密码(该密码是普通用户的密码),从root用户切换到普通用户不需要密码。
成功之后的终端
再执行上述命令,还是提示找不到编译器
因为普通用户设置好的环境变量在 root 用户上面是不生效的。这个时候先尝试一下如下命令,不用 sudo 去编译
make vexpress_ca9x4_defconfig ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-
生成配置文件日志
tyustli@tyustli-machine:~/code/open_source/u-boot$ make vexpress_ca9x4_defconfig ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-
#
# configuration written to .config
#
OK 了。。。
在 /etc/profile 文件中
PATH=$PATH:/home/tyustli/cross_tool/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin
这里设置当前用户的PATH,而sudo执行make的时候,使用的是超级用户权限,那也就使用了超级用户的PATH,但是这个PATH里,并没有 /home/tyustli/cross_tool/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin
解决方法:
su [用户密码]
在当前 shell 下,设置环境变量:
PATH=$PATH:/home/tyustli/cross_tool/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin
再去编译,就可以找到 arm-none-linux-gcc 了
报错情况2
如果安装了 arm-none-linux-gnueabi-工具链, arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc -v 无法显示出版本信息,
- 可能是因为 ubuntu 为64位的,需要安装32位的运行库。
sudo apt-get install build-essential pkg-config zlib1g-dev libglib2.0-0 libglib2.0-dev libsdl1.2-dev libpixman-1-dev libfdt-dev autoconf automake libtool librbd-dev libaio-dev flex bison -y
sudo apt-get install lib32ncurses5-dev
sudo apt-get install lib32z1
sudo apt-get install libgl1-mesa-dri:i386
sudo apt-get install ia32-libs-multiarch:i386
...
- 也可能是编译器路径没有添加到环境变量,参考:https://blog.csdn.net/tyustli/article/details/122980985
u-boot 配置
使用命令
make vexpress_ca9x4_defconfig ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-
可以生成 u-boot 的默认配置,如果想自己裁剪 u-boot,那就需要手动配置 u-boot
命令行输入
make menuconfig
关于 u-boot 的配置后续再介绍,这里只介绍如何进入配置界面。
esc 退出配置界面
编译
编译脚本
export ARCH=arm
export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-
make clean && make vexpress_ca9x4_defconfig
make -j6
使用命令 chmod 777 my_build.sh 给予执行权限
编译报错解决
fatal error: openssl/evp.h: No such file or directory # include <openssl/evp.h>
解决方法
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev
编译日志
CC lib/lmb.oCC lib/membuff.oCC lib/slre.oCC lib/string.oLD lib/efi_loader/dtbdump_efi.soLD lib/efi_loader/initrddump_efi.soCC lib/tables_csum.oOBJCOPY lib/efi_loader/dtbdump.efiOBJCOPY lib/efi_loader/initrddump.efiCC lib/time.oCC lib/hexdump.oCC lib/uuid.oCC lib/rand.oCC lib/panic.oCC lib/vsprintf.oCC lib/strto.oCC lib/abuf.oCC lib/date.oCC lib/rtc-lib.oCC lib/elf.oAR lib/built-in.oLD u-bootOBJCOPY u-boot.srecOBJCOPY u-boot-nodtb.binSYM u-boot.symCOPY u-boot.bin
===================== WARNING ======================
CONFIG_OF_EMBED is enabled. This option should only
be used for debugging purposes. Please use
CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE for boards in mainline.
See doc/develop/devicetree/control.rst for more info.
====================================================
===================== WARNING ======================
This board does not use CONFIG_DM_SERIAL (Driver Model
for Serial drivers). Please update the board to use
CONFIG_DM_SERIAL before the v2023.04 release. Failure to
update by the deadline may result in board removal.
See doc/develop/driver-model/migration.rst for more info.
====================================================OFCHK .config
编译产物
api board cmd config.mk disk drivers env fs Kbuild lib MAINTAINERS my_build.sh post scripts test u-boot u-boot.cfg u-boot.map u-boot.srec
arch boot common configs doc dts examples include Kconfig Licenses Makefile net README System.map tools u-boot.bin u-boot.lds u-boot-nodtb.bin u-boot.sym
运行
qemu 运行与安装参考:https://blog.csdn.net/tyustli/article/details/130461323
qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -m 256 -kernel ./u-boot -nographic
- -nographic 表示不使用图形化界面,仅仅使用串口(如果没有这个选项,u-boot 程序无法正常运行)
- 输入 ctrl + A 后按 X 退出 QEMU
效果
tyustli@tyustli-machine:~/code/open_source/u-boot$ qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -m 256 -kernel ./u-boot -nographic
pulseaudio: set_sink_input_volume() failed
pulseaudio: Reason: Invalid argument
pulseaudio: set_sink_input_mute() failed
pulseaudio: Reason: Invalid argumentU-Boot 2023.10-00813-g997bef3c6d (Oct 12 2023 - 21:45:33 +0800)DRAM: 256 MiB
WARNING: Caches not enabled
Core: 18 devices, 10 uclasses, devicetree: embed
Flash: 128 MiB
MMC: mmci@5000: 0
Loading Environment from Flash... *** Warning - bad CRC, using default environmentIn: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Net: eth0: ethernet@3,02000000
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
=>
=> ls
ls - list files in a directory (default /)Usage:
ls <interface> [<dev[:part]> [directory]]- List files in directory 'directory' of partition 'part' ondevice type 'interface' instance 'dev'.
=>
Hit any key to stop autoboot
这个倒计时是用来启动 linux 的,如果几秒内终端没有输入任何命令,就会自动启动 linux ,目前只有 u-boot 所以按下任意键结束倒计时,进入 u-boot 的命令行模式。当然,如果不输入任何信息,倒计时结束,u-boot 去启动 linux ,但是由于没有 linux 镜像文件会导致启动失败,还是会进入 u-boot 的命令行。
下面是倒计时超时,启动 linux 失败,进入 u-boot 的命令行的日志
BOOTP broadcast 1
DHCP client bound to address 10.0.2.15 (3 ms)
*** Warning: no boot file name; using '0A00020F.img'
Using ethernet@3,02000000 device
TFTP from server 10.0.2.2; our IP address is 10.0.2.15
Filename '0A00020F.img'.
Load address: 0x60100000
Loading: *
TFTP error: 'Access violation' (2)
Not retrying...
smc911x: MAC 52:54:00:12:34:56
missing environment variable: pxefile_addr_r
smc911x: detected LAN9118 controller
smc911x: phy initialized
smc911x: MAC 52:54:00:12:34:56
BOOTP broadcast 1
DHCP client bound to address 10.0.2.15 (1 ms)
Using ethernet@3,02000000 device
TFTP from server 10.0.2.2; our IP address is 10.0.2.15
Filename 'boot.scr.uimg'.
Load address: 0x60100000
Loading: *
TFTP error: 'Access violation' (2)
Not retrying...
smc911x: MAC 52:54:00:12:34:56
smc911x: detected LAN9118 controller
smc911x: phy initialized
smc911x: MAC 52:54:00:12:34:56
BOOTP broadcast 1
DHCP client bound to address 10.0.2.15 (1 ms)
Using ethernet@3,02000000 device
TFTP from server 10.0.2.2; our IP address is 10.0.2.15
Filename 'boot.scr.uimg'.
Load address: 0x60100000
Loading: *
TFTP error: 'Access violation' (2)
Not retrying...
smc911x: MAC 52:54:00:12:34:56
cp - memory copyUsage:
cp [.b, .w, .l, .q] source target count
Wrong Image Format for bootm command
ERROR: can't get kernel image!
=>
