网站管理人员队伍建设有待加强互联网营销师国家职业技能标准
导读:AI大模型日报,爬虫+LLM自动生成,一文览尽每日AI大模型要点资讯!
目前采用“文心一言”(ERNIE-4.0-8K-latest)生成了今日要点以及每条资讯的摘要。欢迎阅读!
《AI大模型日报》今日要点:今日AI大模型领域的资讯涵盖了多模态新基准的提出、从容大模型在多模态评测中的卓越表现、谷歌开源的Gemma 2模型、字节大模型团队的Depth Anything V2模型被苹果选中、科大讯飞发布的星火大模型V4.0的重大突破、尤洋团队实现的AI实时生成视频、OpenAI的CriticGPT新模型、LeCun和谢赛宁提出的视觉多模态模型Cambrian-1,以及智源大会上关于视觉大模型的探讨。这些报道共同展现了AI大模型在模拟人类推理、多模态能力、效率与经济性、集成应用等方面的快速发展,同时也指出了模型在复杂推理、视觉表征等方面的挑战与机遇。各大科技企业和研究团队通过不断创新,推动AI大模型向更高效、更强大、更贴近人类需求的方向发展。
标题: Bengio团队提出多模态新基准,直指Claude 3.5和GPT-4o弱点

摘要: 本文作者张天宇聚焦于多模态、GFlowNet、多智能体强化学习等,已在多个机器学习顶会发表论文。文章探讨实现通用人工智能AGI的关键在于模拟人类的思考和推理过程,引入视觉字幕恢复(VCR)任务来评估视觉语言模型的推理能力。VCR任务要求模型填补被遮挡的文字,而当前大多数模型在此任务上表现不佳,尤其在困难模式下。这表明模型在模拟人类复杂推理过程方面仍有很长的路要走。
网址: Bengio团队提出多模态新基准,直指Claude 3.5和GPT-4o弱点 | 机器之心
标题: 击败Gemini-1.5-Pro、GPT-4V,从容大模型多模态能力跻身全球前三
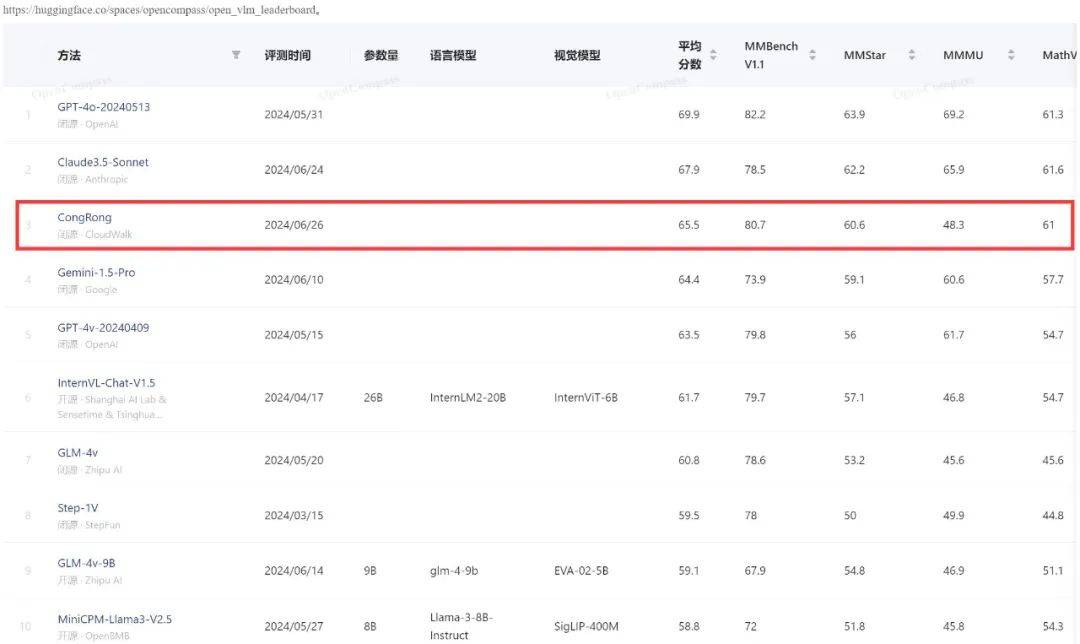
摘要: 云从科技的从容大模型在OpenCompass多模态评测中取得重大进展,平均得分65.5,跻身全球前三。在国内市场,该模型排名第一。从容大模型在6个数据集上表现优异,尤其在OCRBench测试集上获得全球最高分。这一成就归功于云从科技自研的高效多模态处理架构和先进的计算技术,及其在视觉、语言领域的深厚积累。此前,从容大模型已在视觉、跨模态领域多次刷新世界纪录。此次表现不仅证明了云从科技的技术实力,也为全球科技企业在AI竞争中树立了典范。
网址: 击败Gemini-1.5-Pro、GPT-4V,从容大模型多模态能力跻身全球前三 | 机器之心
标题: 谷歌「诚意之作」,开源9B、27B版Gemma2,主打高效、经济!
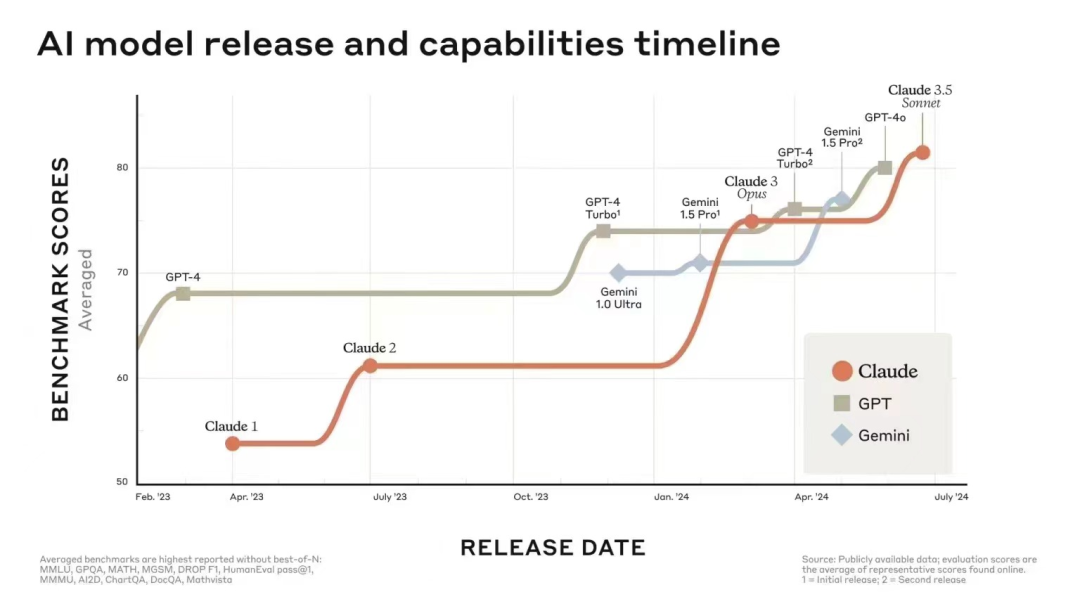
摘要: 谷歌推出Gemma 2,性能翻倍,可与更大模型竞争。Gemma 2提供9B和27B参数版本,推理性能和效率优于第一代,且成本降低。其27B模型性能卓越,9B模型也超越同类。Gemma 2易于集成,兼容多框架,可通过Google Cloud轻松部署。还有新的Gemma Cookbook和上下文缓存功能助力开发者。模型基于仅解码器transformer架构,交替使用局部和全局注意力,采用logit软封顶。谷歌开放Gemma 2,旨在普及AI工具。
网址: 谷歌「诚意之作」,开源9B、27B版Gemma2,主打高效、经济! | 机器之心
标题: 字节大模型团队Depth Anything V2模型入选苹果最新CoreML模型
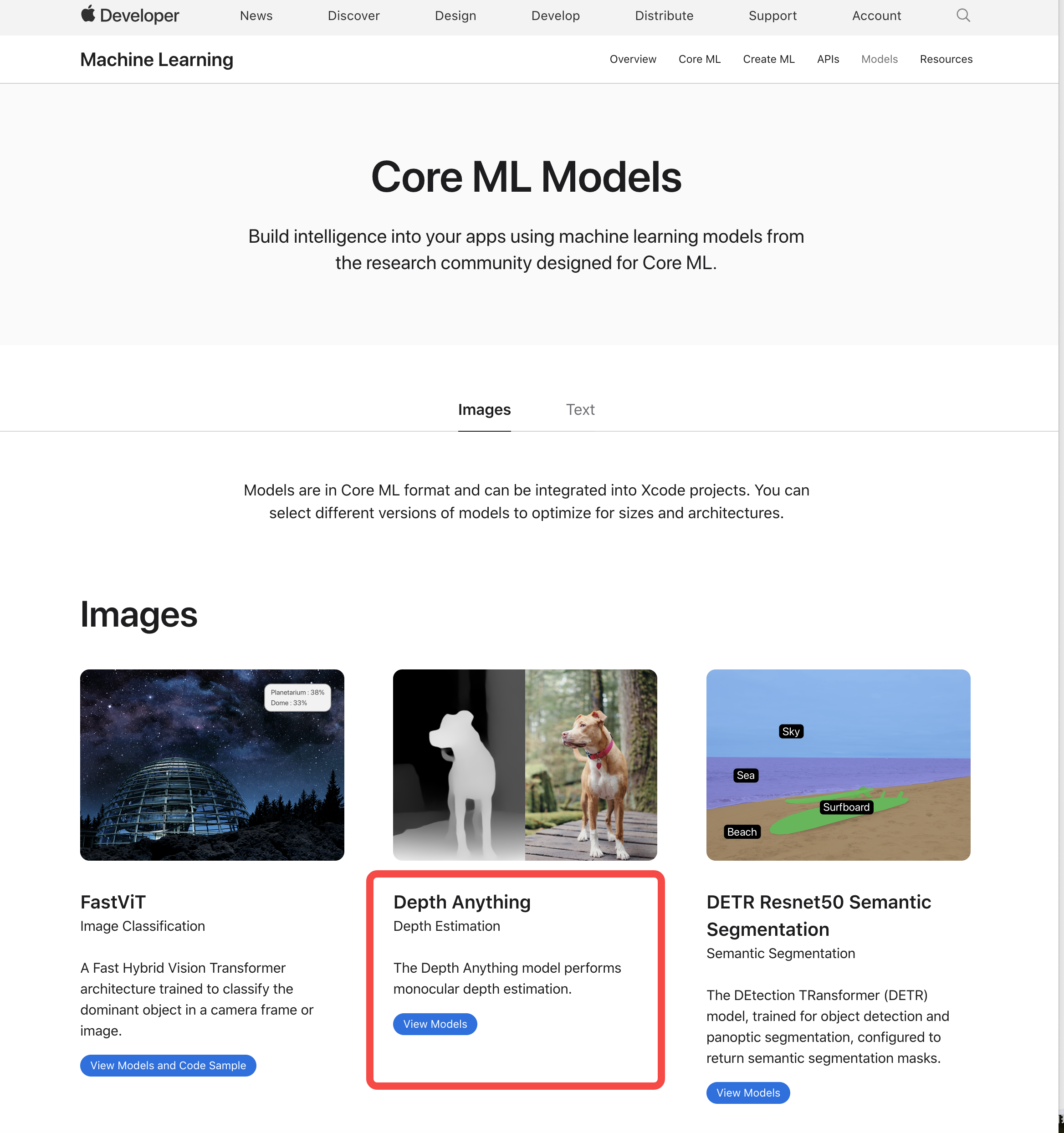
摘要: 苹果公司近日在HuggingFace上发布了20个新Core ML模型和4个数据集,其中包括字节大模型团队的单目深度估计模型Depth Anything V2。Core ML是苹果的机器学习框架,可集成模型到iOS、MacOS等设备,高效运行复杂的AI任务,增强用户隐私,减少延迟。Depth Anything V2在细节处理上更精细,鲁棒性更强,速度提升显著。该模型可应用于多个领域,如自动驾驶等。新发布的Core ML模型涵盖多个领域,开发者可使用coremltools转换模型格式,优化设备性能,减少内存占用和功耗。
网址: 字节大模型团队Depth Anything V2模型入选苹果最新CoreML模型 | 机器之心
标题: 国产大模型新高度!讯飞星火4.0发布:整体超越GPT-4 Turbo,8个国际权威测试集测评第一

摘要: 科大讯飞发布讯飞星火大模型V4.0,该模型在医疗、教育等领域有重大突破,整体性能超越GPT-4 Turbo,成为国内领先的大模型。V4.0在文本生成、语言理解等七大核心能力上全面升级,并在多个国际测试中排名第一。此外,星火大模型还加强了复杂指令跟随和长文本处理能力,并推出新功能——长文本内容溯源,提高了答案准确率。在多模态方面,星火大模型V4.0的图文识别能力持续升级,超越了OpenAI的最新旗舰模型。语音能力也是科大讯飞的绝对优势,V4.0增加了对37种方言的识别,实现了74种语言免切-自由交流。同时,讯飞还展示了超复杂场景语音转写的能力。在医疗领域,讯飞推出了医疗大模型「讯飞晓医」,可以为普通用户提供病历、体检报告解读等服务。在教育领域,讯飞发布了星火智能批阅机和升级后的AI学习机,提高了教育效率。此外,讯飞还推出了「个人空间」,打造懂你的AI助手。
网址: 国产大模型新高度!讯飞星火4.0发布:整体超越GPT-4 Turbo,8个国际权威测试集测评第一 | 机器之心
标题: AI首次实时生成视频!尤洋团队新作,网友:这是新纪元
摘要: AI实时生成视频的新纪元已经到来!尤洋团队推出了首个基于DiT的实时视频生成方法——Pyramid Attention Broadcast(PAB)。该方法通过减少冗余注意力计算,实现了高达21.6FPS和10.6倍加速,同时保持了视频生成模型的质量。PAB作为一种免训练方法,可为将来任何基于DiT的视频生成模型提供实时功能。这一创新引来了网友和专业人士的惊叹与好评。团队通过比较不同时间步骤的注意力差异,提出用PAB减少不必要的注意力计算,从而节省计算量。相关研究已公开,该团队由尤洋教授领衔,成员包括赵轩磊、王锴和金小龙。
网址: AI首次实时生成视频!尤洋团队新作,网友:这是新纪元 | 量子位
标题: OpenAI突发新模型:用GPT改进GPT训练,左脚踩右脚登天,RLHF突破人类能力上限
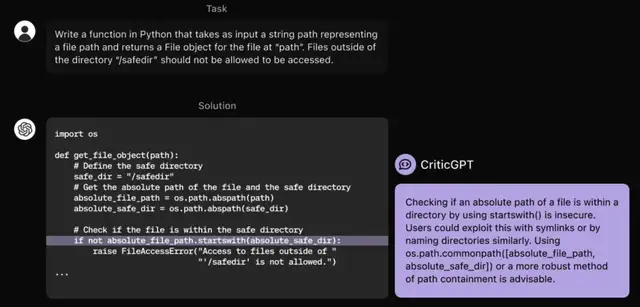
摘要: OpenAI发布了新模型CriticGPT,该模型基于GPT-4训练,旨在改进下一代GPT训练。CriticGPT在代码挑错方面表现出色,能找到75%以上的Bug,远超人类的25%,且其评论更受人类训练师青睐。该模型还能泛化到代码之外的任务,如RLHF训练中的AI输出挑错,并已进入OpenAI内部训练流程。CriticGPT的成功意味着AI在挑错能力上有望突破人类上限,实现自我改进。该研究由前超级对齐团队负责人Jan Leike带队,虽已解散,但成果仍具重要意义。同时,OpenAI还发布了相关论文,展示了其研究诚意。
网址: OpenAI突发新模型:用GPT改进GPT训练,左脚踩右脚登天,RLHF突破人类能力上限 | 量子位
标题: LeCun谢赛宁首发全新视觉多模态模型,等效1000张A100干翻GPT-4V

摘要: 近日,由LeCun和谢赛宁等大佬共同提出了全新的SOTA MLLM——Cambrian-1,该模型以视觉为中心设计多模态模型,并全面开源了相关权重、代码、数据集及微调评估方法。Cambrian-1围绕五个关键方面构建,包括视觉表示、连接器设计、指令微调数据、指令微调策略和实践以及基准测试,旨在弥补多模态学习中视觉研究的不足,打破语言依赖的瓶颈。模型采用MLLM指令微调作为评估协议,强调视觉问答在解决现实世界感知任务中的重要性。研究团队通过谷歌TPU训练,展示了该模型在视觉表征能力上的优势,并呼吁学界业界共同推进以视觉为中心的多模态学习研究。此外,项目还得到了Jeff Dean和Demis Hassabis等业界大佬的支持。
网址: LeCun谢赛宁首发全新视觉多模态模型,等效1000张A100干翻GPT-4V - 智源社区
标题: 视觉重回第一赛道?颜水成领衔视觉大模型论坛丨2024智源大会回顾

摘要: 算法起源于计算机视觉领域,后逐渐迁移至语音、NLP等领域。近年来,随着Transformer的出现,NLP成为新算法发源地,再逐渐应用于视觉领域。今年,计算机视觉似乎重回第一赛道。在智源大会的「视觉大模型」专题论坛上,多位专家探讨了视觉大模型的最新研究成果和实践经验。其中,潞晨科技的申琛惠介绍了Open Sora高效低成本视频生成模型,旨在通过低成本开源方案引入社区,采用基于主流的DiT框架和类似Sora的过程生成视频。生数科技的鲍凡则展示了高保真4D重构模型Vidu4D,该模型采用全球首个Diffusion Transformer融合架构,支持多模态生成式建模和4D表示提取,具有作为世界模拟器的潜力。这些研究展示了视频生成模型在帧真实性和3D一致性方面的优势,以及通过大模型探索世界模型的两条道路。
网址: 视觉重回第一赛道?颜水成领衔视觉大模型论坛丨2024智源大会回顾 - 智源社区
